Content
all pages of web site of Vadym Zayets
(part 1): Basic Spin Properties of electrons 
Landau -Lifshitz Eq.; Spin-orbit interaction; Exchange interaction; Magneto-optics vs. spin; spin vs. orbital moment; What is a hole?; e-Drugs (Electronic drugs). PMA sensor.
(part 2) Spin Properties of gas of conduction electrons 
Spin-polarized/ unpolarized electrons; Spin statistics; Spin Distribution of Conduction electron;. Electron gas of conduction electrons in Magnetic Field Pauli paramagnetism; conduction electrons in a ferromagentic metal
(part 3) Spin Transport 
Transport Eqs.; Spin Proximity/ Spin Injection; Spin Detection; Boltzmann Eqs.; Mean-free path; Current near Interface; Non-local Spin Detection; Thermally-activated magnetization switching, Coercive field; Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect); ll-metal transistor Spin-orbit torque (SOT effect);
(part 4) Current- induced magnetization reversal
. Iteraction of groups of conduction electrons of different spin polarization; Spin-Torque Current. Spin-Transfer Torque; All-metal transistor; Spin-orbit torque (SOT effect); Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect); Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal.
(part 5) Family of Magneto- transport effects 
: Hall effect, Ordinary Hall effect; Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) and Planar Hall effect (making); Spin Hall effect; Inverse Spin Hall effect; Giant magnetic Resistance (GMR) effect. Spin- Dependent Conductivity;. Tunnel Magnetic Resistance (TMR).;Magnetic Tunnel Junction (MTJ) ; MgO-based MTJ; C
(part 6) high- precision measurement method of magnetic and magneto- transport properties of nanomagnets 
Access to all my experimental data of nanomagnet measurement; Measurement of Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE); Measurement of spin polarization; Measurement of Coercive field, Retention time. parameter Δ , size of nucleation domain; RF measurements of magneto-transport effect;s Measurement of SOT-type in- plane magnetic field: " field- like torque" + "damp- like torque"; Measurement of Anisotropy field; Explaination of my EB nanotechnology;Access to Reticle data
(part 7) old model of spin-up/down bands for the spin transport

(The applications of this model are limited, because this model has some incorrect assumption)
(part 8) High- speed optical memory 
FMR vs. Parametric Magnetization Reversal |
|---|
| In the case of Parametric Magnetization Reversal, the precession torque is fully synchronized in both phase and frequency with the magnetization precession. In contrast, Ferromagnetic Resonance (FMR) lacks such synchronization. Consequently, the precession angle remains very small in FMR, whereas it can become large in Parametric Magnetization Reversal—often leading to complete magnetization reversal. (details are here) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Applications; Operational principal; High-speed demultiplexing experiment; Reading method; High-Speed Spin Injection; Spin-photon memory with MTJ; Fabrication Technology; EB nano fabrication; Reticle 10 data
(part 9) Magneto-optical effect 


Optical isolator Faraday rotation angle MCD Measurement of Isolation Kerr rotation High-precision measurement of non-linear refractive index and non-linear optical absorption Origin of Magneto-optics
(part10) Transverse Magneto-Optical effect 


Experimental observation of transverse MO effect; Properties of transverse MO effect; Origin of transverse MO effect; Transverse Ellipticity; Two contributions to transverse MO effect; Magnetization-dependent optical loss; Calculations of transverse MO effect in the case of multilayer structure; Optical excitation of spin-polarized electrons utilizing transverse MO; Plasmons; Giant Enhancement of Transverse MO effect
(part 11) Si Photonics. Plasmonic. 
Plasmonic isolator; Plasmonic modulator; Si nanowire fabrication technology; Si Photonics; Directional coupler; Integration of plasmonic + Si waveguides; ; III-V plasmonic;
(part 12) Personal Data
CV
Publications
Technology
Downloads
Fake, Fraud and Highlight research
| click on image to enlarge it. |
Basic Spin Properties of electrons
Basic properties of electron spin. Spinors.Spin in a magnetic field
Spin Precession. Precession Damping. Landau -Lifshitz equation
What is the Spin?
Spin-Orbit interaction
Exchange interaction
sp-d exchange interaction
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)
e-Drugs (Electronic drugs). PMA sensor.
What is a hole?
Magneto-optics & Electron Spin
Orbital moment. Quenching of orbital moment
Thermally-activated magnetization switching. Coercive field. Retention time. Δ
Heating of a ferromagnet. Curie–Weiss law. Curie Temperature
All-optical magnetization switching
Cosmic inflation + Big Bang |
|---|
| Creation Story of all Matter in the Universe. |
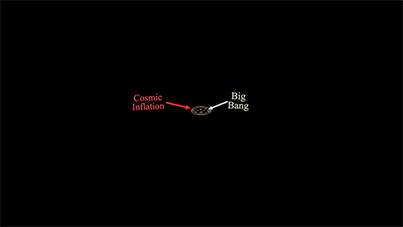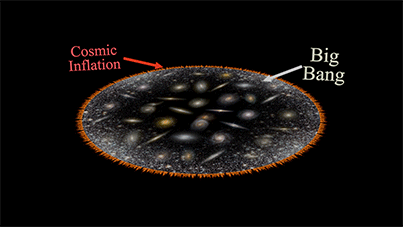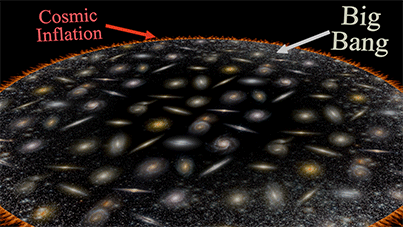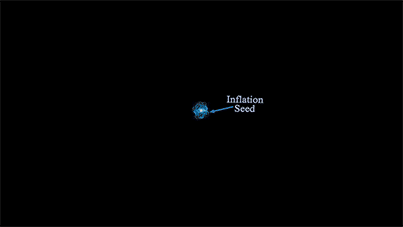 |
| (Inflation Seed): The Inflation Seed refers to the reversible spontaneous breaking of space symmetry (see above), resulting in the creation of a pair of minute particles whose gravitational fields triggered cosmic inflation. It existed only for a very brief period due to its reversible nature. The inflation seed shares similarities with the reversible spontaneous breaking that gives rise to dark energy (see above). |
| (Cosmic Inflation): The Cosmic Inflation describes the irreversible and self-sustaining spontaneous breaking of space symmetry, leading to the creation of all matter in our Universe. It occurs within the region of a high gravitational field gradient at the expanding sphere's edge, where matter is continuously created from vacuum. |
| (Big Bang): The Big Bang describes the interaction and transformation of matter created by Cosmic Inflation, culminating in the formation of the Universe as we perceive and inhabit it today, complete with its galaxies, stars, and planets. |
| click here to see more details and explainations |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Spin-dependent optical transition
Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)
Spin-orbit torque (SOT effect). Modulation of magnetic properties by electrical current
All-metal transistor. All- metal LD
Ferromagnetic resonance (FMR). FMR vs. Parametric Magnetization Reversal.
Post- Standard and Standard Models of our Universe & Spin
Parameters of magnetic materials. MgO-based MTJ
 go back to top
go back to top
 Spin Properties of gas of conduction electrons
Spin Properties of gas of conduction electrons
Spin-polarized/ unpolarized electrons
Spin-dependent Scatterings between conduction electrons
Spin statistics. Spin Distribution of Conduction electrons. Fermi-Dirac Energy distribution.
Electron gas of conduction electrons in Magnetic Field
Pauli paramagnetism. Pauli and Stoner models. Features and limitations.
model comparison for spin distribution of the conduction electrons
Questions 1 & Answers (very old)
Introduction (very old)
Questions 2 & Answers (very old)
 go back to top
go back to top
Doing the Science has never been easy |
 |
In contrast, the production of fakes in a larger numbers is much easier |
| Click on image to enlarge it |
Spin Transport 
Introduction
Transport Eqs.
Spin Proximity/ Spin Injection
Spin Detection
Boltzmann Eqs.
Electrical current. Non-magnetic material (New)
Electrical current. Magnetic material
Scattering current
Mean-free path
Current near Interface
Non-local Spin Detection
 Current- induced magnetization reversal
Current- induced magnetization reversal 
Spin rotation of gas of conduction electrons
Spin Torque for Conduction electrons. Iteraction of groups of conduction electrons of different spin polarization
Spin-Torque Current.
Spin-Transfer Torque
All-metal transistor. All- metal LD
Spin-orbit torque (SOT effect). Modulation of magnetic properties by electrical current
Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)
Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal.
Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal. Part.1: General.
Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal. Part 2. Parametric parameter : Current- induced magnetic field.
Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal. Part 3. Parametric parameter: Anisotropy field.
Parametric mechanism of Magnetization Reversal. Part 4. Parametric parameter: Spin Injection
 Family of Magneto- transport effects: Hall effect, AMR, spin-dependent conductivity
Family of Magneto- transport effects: Hall effect, AMR, spin-dependent conductivity
Family of Hall and AMR effects
Ordinary Hall effect
Anomalous Hall effect (AHE)
Anisotropic magnetoresistance/ Planar Hall effect (AMR/PHE)
Spin Hall effect
Inverse Spin Hall effect
Giant magnetic Resistance (GMR) effect. Spin- Dependent Conductivity.
Tunnel Magnetic Resistance (TMR). Magnetic Tunnel Junction (MTJ)
Parameters of magnetic materials. MgO-based MTJ
Charge accumulation at MTJ, at a contact between two metals
 high- precision measurement method of magnetic and magneto- transport properties of nanomagnets
high- precision measurement method of magnetic and magneto- transport properties of nanomagnets
All measurement Data .  Properties of FeCoB nanomagnets
Properties of FeCoB nanomagnets
Measurement methods of Magnetic properties of nanomagnets.
Measurement of strength of Spin-Orbit Interaction
Measurement of Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE). Measurement of spin polarization
Measurement of Coercive field, Retention time. parameter Δ , size of nucleation domain
RF measurements of magneto-transport effects
Measurement of SOT-type in- plane magnetic field: " field- like torque" + "damp- like torque"
Measurement of Anisotropy field
EB nanotechnology
Reticle 11
old model of spin-up/down bands of the spin transport 

(The applications of this model are limited, because this model has some incorrect assumption)
Introduction
Basic Transport equations
Spin and charge currents
Spin drain
Non-magnetic metals
Ferromagnetic metals
Semiconductors (Basic)
Threshold spin current
Spin gain/damping
Spin Relaxation
Spin Hall/ Inverse Spin Hall effects
ee- interaction

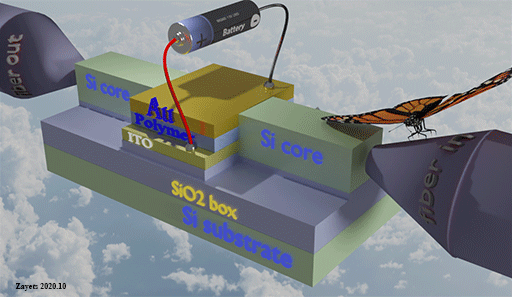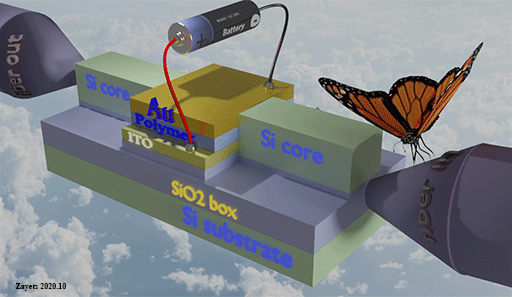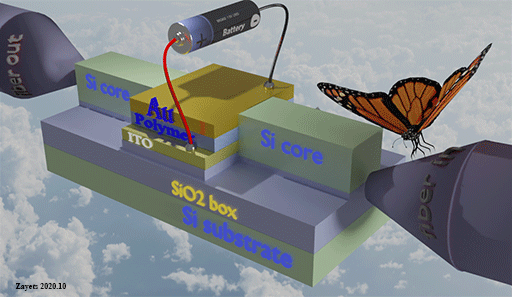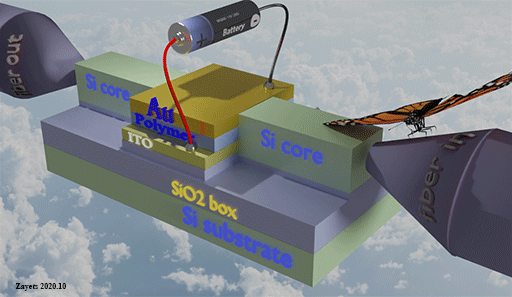
High- speed optical memory 
This topic is about my development of high-speed non-volatile optical memory
Introduction
Applications
Operational principal
High-speed demultiplexing experiment
Reading
High-Speed Spin Injection
Spin-photon memory with MTJ
Fabrication Technology
EB nano fabrication
Reticle 10
Differential modulator
All-optical magnetization switching
Magneto-optical effect 


Optical isolator
Faraday rotation angle
MCD
Measurement of Isolation
Kerr rotation
High-precision measurement of non-linear refractive index and non-linear optical absorption
Origin of Magneto-optics
 |
| Optical isolator blocks back propagating light |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Transverse Magneto-Optical effect 


Introduction
Experimental observation of transverse MO effect
Properties of transverse MO effect
Origin of transverse MO effect
Transverse Ellipticity
Two contributions to transverse MO effect
Magnetization-dependent optical loss
Calculations of transverse MO effect in the case of multilayer structure
Optical excitation of spin-polarized electrons utilizing transverse MO
Plasmons
Giant Enhancement of Transverse MO effect
History and Future
Silicon Photonics. Plasmonic 
Si nanowire waveguide
Si nanowire waveguide. Basic properties.
Si nanowire fabrication technology
fiber/waveguide coupling setup
devices made of Si-waveguides
directional coupler
Two Photon Absorption in Si nanowire waveguide
AlGAAs passive waveguide
AlGaAs waveguide (800 nm)
AlGaAs waveguide (1550 nm)
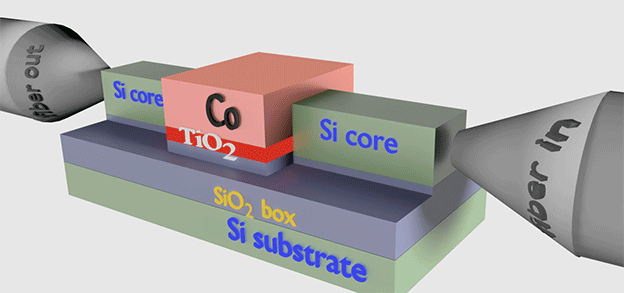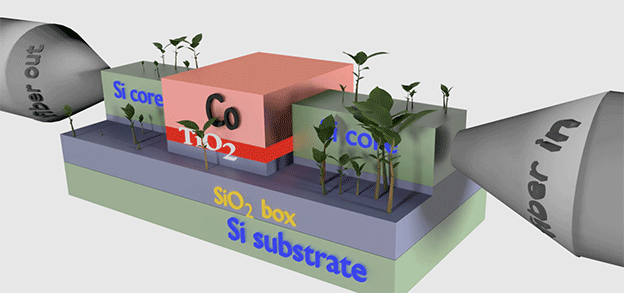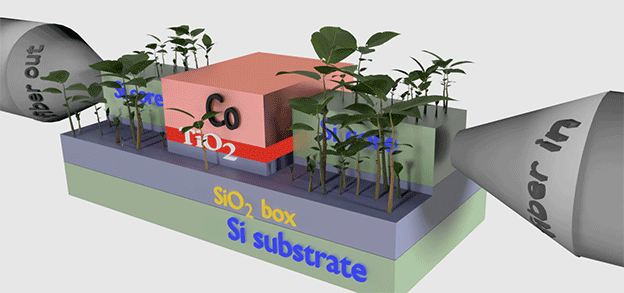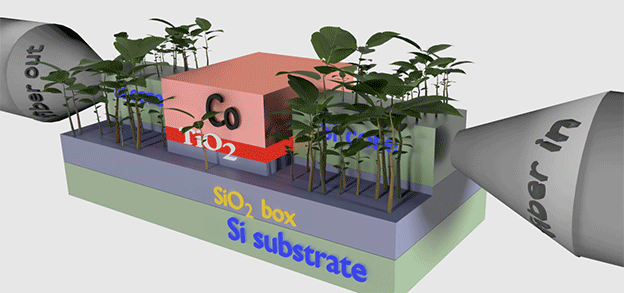 |
| Plasmonic isolator |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Plasmonic
Plasmonic. Introduction
Misconception about “plasmonic- friendly” and “plasmonic- unfriendly” metal material
integration: plasmonic + Si waveguides
Comparison of two technologies of Integration of Si nanowire waveguide and plasmonic waveguide
Out-plane plasmonic confinement
plasmonic isolator
III-V plasmonic
plasmonic on GaAs (800 nm)
plasmonic on GaAs (1550 nm)
plasmonic on Si (1550 nm)
plasmons in metal strip
in-plane confinement of plasmons
samples very old