Dr. Vadym Zayets
v.zayets(at)gmail.com
My Research and Inventions
click here to see all content |

Dr. Vadym Zayetsv.zayets(at)gmail.com |
|
 |
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
|
Anomalous Hall effect (AHE)
Spin and Charge TransportAbstract:The Anomalous Hall effect describes the fact that when an electrical current flows in a ferromagnetic metallic wire, an electrical current flows perpendicularly to the wire due to the magnetization of the ferromagnetic wire. The effect is originated from a magnetic interaction of orbital moment on conduction electrons with spin of localized localized electrons.
Note: All data of this page represent only my personal point of view, which are based on my experimental and theoretical research.
|
Measurement of the Hall effect |
||||||
|
||||||
click on image to enlarge it |
(1st contribution): ![]() (Ordinary Hall effect)
(Ordinary Hall effect) ![]() due to magnetic field H inside of the metallic wire
due to magnetic field H inside of the metallic wire
(origin of effect):  The Lorentz force, which conduction electrons experience when moving in a magnetic field (See details origin of the Ordinary Hall effect here)
The Lorentz force, which conduction electrons experience when moving in a magnetic field (See details origin of the Ordinary Hall effect here)
(proportionality to external magnetic field): ![]() The Hall angle αOHE linearly depends on external magnetic field H.
The Hall angle αOHE linearly depends on external magnetic field H.
(affected group of conduction electrons): 

 all conduction electrons (spin- polarized + spin- unpolarized)
all conduction electrons (spin- polarized + spin- unpolarized)
(strength of contribution): ![]() weak
weak ![]() . E.g. αOHE~ 0.2-0.8 mdeg/kG for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
. E.g. αOHE~ 0.2-0.8 mdeg/kG for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(2nd contribution):![]() (Anomalous Hall effect) due to magnetic moments of localized electrons or magnetization M
(Anomalous Hall effect) due to magnetic moments of localized electrons or magnetization M
(origin of effect):  spin-orbit interaction (plus maybe the exchange interaction???). The origin is not fully clear yet.
spin-orbit interaction (plus maybe the exchange interaction???). The origin is not fully clear yet.
(proportionality to external magnetic field): ![]() The Hall angle αAHE does not depends on external magnetic field H. It is a constant vs H.
The Hall angle αAHE does not depends on external magnetic field H. It is a constant vs H.
(affected group of conduction electrons): 

 all conduction electrons (spin- polarized + spin- unpolarized)
all conduction electrons (spin- polarized + spin- unpolarized)
(strength of contribution):![]() strong .
strong .![]() E.g. αAHE~ 300-1500 mdeg for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
E.g. αAHE~ 300-1500 mdeg for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(3d contribution): ![]() (Inverse Spin Hall effect) due to magnetic moments of conduction electrons or the spin polarization of conduction electrons
(Inverse Spin Hall effect) due to magnetic moments of conduction electrons or the spin polarization of conduction electrons
(origin of effect):  Spin-orbit interaction. The Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE) describes the fact that a current of spin- polarized electrons creates an electrical current, which flows perpendicularly to the spin current. Conduction electrons in a ferromagnetic metal are spin- polarized. Asa result, there is a charge current perpendicular to a current of spin- polarized conduction electrons, which flows along a ferromagnetic wire. See details about Spin Hall effect and ISHE here.
Spin-orbit interaction. The Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE) describes the fact that a current of spin- polarized electrons creates an electrical current, which flows perpendicularly to the spin current. Conduction electrons in a ferromagnetic metal are spin- polarized. Asa result, there is a charge current perpendicular to a current of spin- polarized conduction electrons, which flows along a ferromagnetic wire. See details about Spin Hall effect and ISHE here.
(proportionality to external magnetic field): ![]() The Hall angle αISHE non- linearly depends on external magnetic field H. (See details here).
The Hall angle αISHE non- linearly depends on external magnetic field H. (See details here).
(affected group of conduction electrons): ![]()
![]()
![]() only spin-polarized electrons!!! spin- unpolarized conduction electrons do not contribute to this effect (See here)
only spin-polarized electrons!!! spin- unpolarized conduction electrons do not contribute to this effect (See here)
(strength of contribution):![]() moderate .
moderate .![]() E.g. αISHE~ 5-30 mdeg for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
E.g. αISHE~ 5-30 mdeg for FeCoB nanomagnets, which I have studied
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
types of the Hall effect |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| click on image to enlarge it. Zayets 2020.03 |

(Origin 1):
![]() Spin- orbit interaction (SO):
Spin- orbit interaction (SO):
Origin of Anomalous Hall effect: Magnetic interaction of localized and conduction electrons |
||||
The Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) describes the current of conduction electrons, which is created perpendicularly to an electrical current in a ferromagnetic metallic wire due to the spins of the localized d- electrons. The AHE exists due to the magnetic interaction of localized and conduction electrons. Additionally to the movement along the crystal lattice, a conduction electron rotates around each atomic nucleus. It is the reason for the interaction between the steady localized d-electrons and the moving conduction electrons. |
||||
|
||||
(possible origin 1 of AHE): exchange interaction between conduction electron and localized d- electron. The exchange interaction is due to the overlap of wavefunctions of the conduction electron and the localized d- electrons |
||||
(possible origin 2 of AHE): spin- orbit interaction. The magnetic field (spin) of a localized d-electron modifies the orbital symmetry of the conduction electron and therefore enhances the magnetic field HSO of spin- orbit interaction. The HSO makes the scattering of conduction electrons the direction dependent, which results to the perpendicular electrical current (the same as in the case of the Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE)) |
||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
(1st proposal) of the SO as the origin of AHE: Karplus,Luttinger (1954). They used the same formalism as the formalism of the Ordinary Hall effect, but replacing the Lorentz force by the SO. It an incorrect approach since the SO cannot break the time-inverse symmetry and cannot contribute in the similar way. The used approximation was too rough. The error was correctly noticed by Smit (1955), but the error was not accepted by Luttinger (1958).
(2d proposal): skew scatterings: Smit (1955), Smit(1958)
It correctly describes the fact that the SO makes the scattering probability dependent on the electron movement direction and electron spin.
(3d proposal): side-jump scatterings Berger (1970)
It correctly describes the fact that the SO makes the scattering probability different on whether a scattered conduction electron shifted to left or to the right with respect to its initial position
-----------------------------------
(Origin 2):
![]() sp-d exchange interaction:
sp-d exchange interaction:
(1st proposal) by Kondo (1962), which is based on 3 assumptions:
assumption 1: AHE is originated from the sp-d exchange interaction, but not from the spin- orbit interaction
assumption 2: the sp-d exchange interaction depends on velocity (wave vector) of a conduction electron.
assumption 3 (toughest) : the sp-d exchange interaction is different for opposite movement directions of a conduction electron
(2nd modification) by Giovannini (1973)
An additional contribution to the sp-d exchange interaction was assumed in order to explain why the sp-d exchange interaction is different for opposite movement directions of a conduction electron
------------------------------
![]() There were many science- fiction proposals on the origin of AHE. One example is that the AHE is originated by the super conductivity. Such proposals are clearly unrealistic and they will not be discussed here
There were many science- fiction proposals on the origin of AHE. One example is that the AHE is originated by the super conductivity. Such proposals are clearly unrealistic and they will not be discussed here
Two similar Hall effects: Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) and Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE) |
Both the AHE and ISHE effects describes the current of conduction electrons, which is created perpendicularly to an electrical current in a ferromagnetic metallic wire (Hall effect). The spins of localized d- electrons (magnetization) is responsible for AHE effect. The spins of conduction electrons (spin polarization) is responsible for ISHE effect. |
(difference 1 between AHE and ISHE effects): All conduction electrons (spin- polarized + spin- unpolarized) contribute to the AHE, but only spin- polarized conduction electrons contribute to the ISHE. |
(difference 2 between AHE and ISHE effects): The AHE is proportional to perpendicular component of the total spin of all localized d- electrons. The ISHE is proportional to perpendicular component of the total spin of all spin- polarized conduction electrons. |
| note: in equilibrium the total spins of localized and conduction electrons are parallel |
| click on image to enlarge it |
The Hall and the Hall angle is measured by a pair of electrodes (See Fig.). Even a slight spacial misalignment of electrodes with respect to each other causes a voltage between electrodes due to the voltage gradient along the wire. This voltage is independent on H and M. In contrast, the Hall voltage and the Hall angle αHall is asymmetrical with respect to H reversal and M reversal. Therefore, it defines as a difference of αHall measured at opposite H:
![]()
From Eq. (3.1), the measured Hall angle can be only proportional to material parameters, which reverse their sign when the H is reversed. Additionally to H itself, there are two more such parameters. The first parameter is the total magnetic moment Md of localized d-electrons. The second parameter is the total magnetic moment Mcond of conduction electrons. Therefore, the Hall angle αHall can be calculated as
![]()
where the 1st term βOHE·H describes proportionality of αHall to external magnetic field ( ordinary Hall effect.); the 2nd term βAHE·M describes proportionality of αHall to magnetization of the ferromagnetic metal (Anomalous Hall effect); the 3d term βISHE· describes proportionality of αHall to the spin polarization of the conduction electrons ( Inverse Spin Hall effect)
Since the magnetization is defined as the total spin of localized electrons , the AHE should be proportional to magnetic properties of localized electrons
Since the electrical current is a flow of conduction electrons, the AHE should be proportional to magnetic properties of conduction electrons
αHall, magnetization Md (total spin of localized electrons), Mcond (total spin of conduction electrons) have the same polarity. They all change their sign when a large external magnetic field H is reversed. As a result, both the Md , Mcond are reversed and the following relations are forbidden:
where k is a constant independent on H. Mcond is linearly proportional to the number of spin- polarized electrons or spin polarization sp
The Uniqueness of the Anomalous Hall effect (AHE) is that is determined by the magnetic properties of two different groups of electrons: the group of conduction electrons and group of localized d- electrons.
As a result, the AHE should be originated from a magnetic interaction between localized d- electrons and conduction electrons. There are three possible interactions between localized and conduction electrons:
(interaction 1 between localized and conduction electrons): ![]() Magneto- static interaction
Magneto- static interaction
(interaction 2 between localized and conduction electrons): ![]() sp-d exchange interaction
sp-d exchange interaction
(interaction 3 between localized and conduction electrons): ![]() Spin-orbit interaction
Spin-orbit interaction
 Origin of Anomalous Hall effect. Direction- depend scattering of conduction electrons due direction dependence of their orbital moment
Origin of Anomalous Hall effect. Direction- depend scattering of conduction electrons due direction dependence of their orbital moment Mechanism of Anomolous Hall effect |
||||||
|
||||||
click on image to enlarge it |
Origin of AHE:  Dependence of electron scattering probability on spins of localized electron and the scattering direction.
Dependence of electron scattering probability on spins of localized electron and the scattering direction.

A conduction electron has a orbital moment, which depends on a movement direction and position of the electron. Magnetic field, which created by the spin of localized electrons, interacts with the orbital moment of a conduction electron. The energy is higher when the spin M of localized electron is along the orbital moment of conduction electron and the energy is smaller when M is opposite to the orbital moment. The energy difference makes the scattering probability dependent on M and scattering direction, because of the directional dependence of the orbital moment. The difference in the scattering probabilities creates an electron current (Hall current) perpendicularly to the bias current.
Origin of AHE. ![]() How the spin of localized d- electrons creates an electrical current flowing perpendicularly to a ferromagnetic wire. Step by step explanation
How the spin of localized d- electrons creates an electrical current flowing perpendicularly to a ferromagnetic wire. Step by step explanation![]()
![]() The scattering probability of a conduction electron is different to the left and to the right direction. As a result, more electrons are scattered in one direction and an electrical current flows from the left to the right.
The scattering probability of a conduction electron is different to the left and to the right direction. As a result, more electrons are scattered in one direction and an electrical current flows from the left to the right.
![]() The scattering probability is different because the magnetic energy of a conduction electron is different when its moves to the left and the right directions..
The scattering probability is different because the magnetic energy of a conduction electron is different when its moves to the left and the right directions..
![]() The magnetic energy is proportional to the magnetic field, which is induced by the spins of the localized d- electrons, and the magnetic moment of a conduction electron and therefore the orbital moment of the conduction electron. The orbital moment of a conduction electron is different for its opposite movement direction
The magnetic energy is proportional to the magnetic field, which is induced by the spins of the localized d- electrons, and the magnetic moment of a conduction electron and therefore the orbital moment of the conduction electron. The orbital moment of a conduction electron is different for its opposite movement direction
![]() It is an unique feature of conduction electrons. Details see here.
It is an unique feature of conduction electrons. Details see here.
Spin- Orbit interaction as the origin of Inverse Spin Hall effect (ISHE) |
|||||||||
| The origin of ISHE is the spin- dependent scatterings. There are several mechanisms, which make scatterings of conductions electrons spin- and direction- dependent. (mechanism 1): due to a non-zero orbital moment of conduction electrons; (mechanism 2): Skew scatterings (mechanism 3): Side-jump scatterings at defect (mechanism 4): Side-jump scatterings across an interface. Independently on the mechanism, the origin of ISHE is the same. The conduction electron experiences the magnetic field HSO of the spin-orbit interaction, which depends either on the electron movement direction (kx, ky, kz) or the electron spacial position (x, y, z) . The HSO makes scatterings of conductions electrons spin- and direction- dependent. As a result of the spin- and direction- dependency of scattering probability, the numbers of spin-polarized electrons, which are scattered to the left and to the right, are different and there is an electron current (charge current) flowing perpendicularly to the main current | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| note: |
|||||||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
(problem of Spin- orbit interaction as the origin of AHE): ![]() The Spin- Orbit interaction does induce the Hall effect, but this Hall effect is proportional to the number of the spin-polarized conduction electrons and such effect is called the Inverse Spin Hall effect. The Hall effect due to AHE should be proportional to the total number of the conduction electrons (See forbidden relations here).
The Spin- Orbit interaction does induce the Hall effect, but this Hall effect is proportional to the number of the spin-polarized conduction electrons and such effect is called the Inverse Spin Hall effect. The Hall effect due to AHE should be proportional to the total number of the conduction electrons (See forbidden relations here).
Hall effects due to the Spin- orbit interaction: ![]() (source 1): due to a non-zero orbital moment of conduction electrons;
(source 1): due to a non-zero orbital moment of conduction electrons; ![]() (source 2): Skew scatterings
(source 2): Skew scatterings ![]() (source 3): Side-jump scatterings at defect
(source 3): Side-jump scatterings at defect ![]() (source 4): Side-jump scatterings across an interface. All these origin are due to spin-dependent scatterings and and they are proportional to the number of spin- polarized electrons.
(source 4): Side-jump scatterings across an interface. All these origin are due to spin-dependent scatterings and and they are proportional to the number of spin- polarized electrons.
 Origin of the Inverse Spin Hall effect
Origin of the Inverse Spin Hall effect (in short)
(in short)(step 1) ![]()
![]() The conduction electrons experience the magnetic field HSO of spin- orbit interaction (See here) due to several possible sources: (source 1): A non-zero orbital moment of a conduction electron (Details are here); (source 2): Skew scatterings (Details are here); (source 3): Side- jump scatterings in electrical field of a defect (Details are here); (source 4): Side- jump scatterings across an interface (Details are here); . Important: Each source makes the direction, polarity and magnitude of magnetic field HSO dependent on either moving direction (kx, ky, kz) or spacial coordinates (x, y, z) of a conduction electron
The conduction electrons experience the magnetic field HSO of spin- orbit interaction (See here) due to several possible sources: (source 1): A non-zero orbital moment of a conduction electron (Details are here); (source 2): Skew scatterings (Details are here); (source 3): Side- jump scatterings in electrical field of a defect (Details are here); (source 4): Side- jump scatterings across an interface (Details are here); . Important: Each source makes the direction, polarity and magnitude of magnetic field HSO dependent on either moving direction (kx, ky, kz) or spacial coordinates (x, y, z) of a conduction electron
(step 2) ![]()
![]()
![]() Due to the magnetic interaction of the magnetic field HSO with spin of a conduction electrons, the scatterings of conduction electrons becomes direction- and spin- dependent. The scattering probability is larger when the HSO is along the spin of a conduction electron and it is smaller when the HSO is opposite to the electron spin. E.g. the spin-up electrons are scattered more to the left and the spin-up electrons are scattered more to the right.
Due to the magnetic interaction of the magnetic field HSO with spin of a conduction electrons, the scatterings of conduction electrons becomes direction- and spin- dependent. The scattering probability is larger when the HSO is along the spin of a conduction electron and it is smaller when the HSO is opposite to the electron spin. E.g. the spin-up electrons are scattered more to the left and the spin-up electrons are scattered more to the right.
(step 3) ![]()
![]()
![]()
 The difference in scatterings probabilities creates an electrical current flowing perpendicularly to the main electrical current. Only spin- polarized conduction electrons contribute to this current. E.g. the spin direction of spin- polarized electrons is up. Since there are more spin-up electrons scattered to the left than to the right, the electron current (charge current) flows into the left direction. Therefore, only spin- polarized electrons contribute to the Hall effect.
The difference in scatterings probabilities creates an electrical current flowing perpendicularly to the main electrical current. Only spin- polarized conduction electrons contribute to this current. E.g. the spin direction of spin- polarized electrons is up. Since there are more spin-up electrons scattered to the left than to the right, the electron current (charge current) flows into the left direction. Therefore, only spin- polarized electrons contribute to the Hall effect.
Yes. You are correct. The conduction electrons are spin- polarized, because the spins of the localized d- electrons are aligned in one direction. The mechanism of spin alignment of conduction electrons is called the spin pumping (See here). There are two mechanisms, which aligns the spins of conduction electrons along the spins of localized electrons. (mechanism 1 (usually weaker) ) the exchange interaction between conduction and localized electrons (sp-d exchange interaction); (mechanism 2 (usually stronger) ) the scattering between localized and conduction electrons. The localized electrons, which spins are aligned in one direction, are constantly scattered into the gas of conduction electrons. Therefore, they are constantly injecting the spin into the group of the conduction electrons. Therefore, it is true that the total spin of conduction electrons is proportional to the total spin of localized electrons and the total spin of conduction electrons is aligned to the spins of localized electrons.
However, the localized and conduction electrons are two very different groups of electrons (see here) and their total spins are two independent magnetic parameters. For example, the number of spin polarized conduction electrons can be changed without affecting the localized electrons (the spin injection etc.).
 In fact, the individual contributions of the AHE and ISHE are measured by changing the number of spin- polarized electrons without influence of the localized electrons. The part of Hall angle, which is changing, is the ISHE contribution and the part of Hall angle, which is staying a constant, is the AHE contribution. The spin polarization of conduction electrons can be changed by a spin injection from a neighbor region or by illumination by a circularly- polarized light. The simplest method is the applying an external magnetic field along the magnetization of a nanomagnet. The conduction electrons are aligned along the magnetic field, therefore the spin polarization increases. The spins of localized electron initially aligned along magnetic field, therefore spins of localized electron are not affected by the magnetic field (almost). More details about this measurements are here
In fact, the individual contributions of the AHE and ISHE are measured by changing the number of spin- polarized electrons without influence of the localized electrons. The part of Hall angle, which is changing, is the ISHE contribution and the part of Hall angle, which is staying a constant, is the AHE contribution. The spin polarization of conduction electrons can be changed by a spin injection from a neighbor region or by illumination by a circularly- polarized light. The simplest method is the applying an external magnetic field along the magnetization of a nanomagnet. The conduction electrons are aligned along the magnetic field, therefore the spin polarization increases. The spins of localized electron initially aligned along magnetic field, therefore spins of localized electron are not affected by the magnetic field (almost). More details about this measurements are here![]() final answer: the Hall effect in a ferromagnetic metal independently proportional to the total total spin of localized electrons and the total spin of conduction electrons. As a result, the Hall effect is the sum of the AHE contribution and the ISHE contribution. Each of contribution should be measured individually.
final answer: the Hall effect in a ferromagnetic metal independently proportional to the total total spin of localized electrons and the total spin of conduction electrons. As a result, the Hall effect is the sum of the AHE contribution and the ISHE contribution. Each of contribution should be measured individually.
 Skew scatterings; Side-jump scatterings at defect ; Side-jump scatterings across an interface. are contribute to the Hall effect, but they contribute to the ISHE effect, but not to the AHE effect. It is because these contributions are proportional to the number of spin- polarized conduction electrons, but not to the total number of conduction electrons as it should be in the case of AHE effect.
Skew scatterings; Side-jump scatterings at defect ; Side-jump scatterings across an interface. are contribute to the Hall effect, but they contribute to the ISHE effect, but not to the AHE effect. It is because these contributions are proportional to the number of spin- polarized conduction electrons, but not to the total number of conduction electrons as it should be in the case of AHE effect.sp-d Exchange Interactions a possible Origin of Anomalous Hall effect |
||
Fig.11. The exchange interaction between a moving conduction electron (shown in green) and a nonmoving localized d- electrons (shown in red). |
||
|
||
When the wave function of conduction electron overlaps an atomic nucleus, there a stationary nonmoving part of wavefunction (green circle with arrow), which describes the rotation of the conduction electron around each nucleus |
||
|
||
| The size of a conduction electron (size of its wave function) is relatively large. A conduction electron can cover simultaneously hundreds or thousands of nuclei. | ||
| The size of a conduction electron is substantially larger than the size of a localized electron. | ||
| click on image to enlarge it. Camera moves together with the conduction electron. |
(problem of sp-d exchange interaction as the origin of AHE): ![]() In order for the sp-d exchange interaction to be the AHE origin, the exchange interaction between the localized d- electrons and conduction electrons should have some unique properties. E.g. the strength of the exchange interaction should change significantly when the movement direction of a conduction electron is reversed. The exchange interaction should not depend on the spin of the conduction electron. The physical mechanisms, which might cause these unique properties, are still unclear.
In order for the sp-d exchange interaction to be the AHE origin, the exchange interaction between the localized d- electrons and conduction electrons should have some unique properties. E.g. the strength of the exchange interaction should change significantly when the movement direction of a conduction electron is reversed. The exchange interaction should not depend on the spin of the conduction electron. The physical mechanisms, which might cause these unique properties, are still unclear.
In order for the sp-d exchange several requirements should be satisfied
(possible solution): Simultaneously with the movement along the metal, the conduction electron rotates around many atomic nuclei. The rotation is described by the Bloch function. The rotation is local and is stationary (does not move along metal). The wavefunction overlap of this stationary part with the nonmoving localized d- electron determines the exchange interaction. Even though the magnitude of this nonmoving stationary wavefunction part of the conduction electron is changing in time, in the average over many localized electrons the overlap does not change in time (see Fig.11) and the sp-d exchange interaction is a non-zero and does not change in time
(possible problem): Additionally to magnitude, the phase of a conduction electrons is continuously changing as the electron moves along the metal. The exchange interaction does depend on the phase. When averaged over the phase, the strength of the averaged exchange interaction might be small
(possible solution): The symmetry of the stationary part depends on the electron speed. This fact is described by the kp- model (Luttinger, Kohn (1955)) and is well verified in semiconductors. The strength of the exchange interaction does depend on the symmetry of the stationary part (Bloch function) of the conduction electron and therefore on its speed.
(possible problem): The change of the symmetry vs the electron speed is very small. As a result, the change of strength of the exchange interaction is small as well. It is difficult to explain the strong AHE effect by this small change of the exchange interaction
(possible solution): Both Kondo (1962) and Giovannini (1973) have used some mathematical tricks in order to include such unexpected dependence into the sp-d exchange interaction. It is unclear how realistically these mathematical tricks correspond to the reality.
(possible problem): The exchange interaction is one of most complex effects of the nature. At present, not all its features are fully understood (See here)
(possible solution): The spins of spin- unpolarized electrons is distributed equally in all directions. The dependence of exchange interaction on the spin of the conduction electrons might be averaged out over such distribution.
(possible problem): The spin- polarized electrons contribute to ISHE (not to AHE)?
 At present, it is difficult to clarify whether the sp-d exchange interaction is the main origin of AHE. There are still too many unanswered questions
At present, it is difficult to clarify whether the sp-d exchange interaction is the main origin of AHE. There are still too many unanswered questions
Measurement of Anomalous Hall effect |
||||||
|
||||||
click on image to enlarge it |
The OHE and AHE is measured by the Hall angle αHall. The contributions from AHE and OHE are independent: αHall=αAHE+αOHE
![]() What is better to use the Hall resistance or Hall angle αHall
What is better to use the Hall resistance or Hall angle αHall
A. The Hall angle αHall. It is only correct parameter characterizing the AHE and OHE.
![]() What are merits to use the Hall resistance for measurement of AHE and OHE?
What are merits to use the Hall resistance for measurement of AHE and OHE?
None. It is just a number in the Ohm unit. It has no physical meaning. It depends on the device geometry. It is not a material intrinsic parameter.
![]() What are merits to use Hall angle αHall of measurement of AHE and OHE?
What are merits to use Hall angle αHall of measurement of AHE and OHE?
![]() merit 1: The αHall has a direct physical meaning. It the angle of deviation of electron movement from a straight line along an applied electrical field.
merit 1: The αHall has a direct physical meaning. It the angle of deviation of electron movement from a straight line along an applied electrical field.
![]() merit 2: The αHall is an intrinsic parameter of a material. It does not depend on the device geometry or film structure. The magnitude of the OHE and AHE in different devices and different films should be only compared by comparing their αHall.
merit 2: The αHall is an intrinsic parameter of a material. It does not depend on the device geometry or film structure. The magnitude of the OHE and AHE in different devices and different films should be only compared by comparing their αHall.
The Hall angle αHall is defined as

where σxx and σxy are diagonal and off-diagonal components of the conductivity tensor
nanowire with two pairs of Hall probes |
||||||
|
||||||
click on image to enlarge it |
Single layer film:
In this case the Hall angle αHall is calculated as
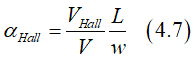
where the Hall voltage VHall, is the Hall voltage L is wire length and w is wire width. The Hall resistance RHall can be calculated
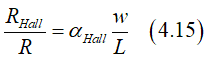
where R is wire resistance
Double-layer metallic wire:
This case when metallic wire consists of two layers: The first layer is made of a ferromagnetic metal. The second layer is made of a non-magnetic metal. In this case the Hall angle αHall of the ferromagnetic metal is calculated as
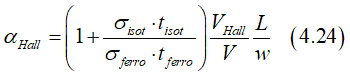
where tferro, tisot, σferro,σisot are thicknesses and conductivities of ferromagnetic and non-magnetic metals.
or the intristic Hall angle αHall,ferro in a ferromagnetic metal is calculated from the measured Hall angle αHall,measured in a double layer nanowire as
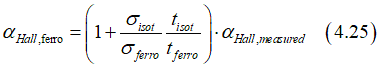
Due to the Hall effect there is an electrical current current across the metallic wire, which can be calculated as
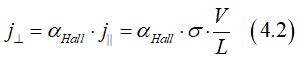
where V is the bias voltage, L is wire length, j|| and j⊥ is current density along and across the wire .
The current j⊥ makes a charge accumulation at walls of the metallic wire. This charge induces the voltage, which is called the Hall voltage VHall. The Hall voltage induces the current, which is opposite to j⊥. The current density of this current j⊥,comp can be calculated as
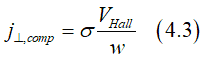
where w is the width of the wire. In total, there is no current across the wire, σ=σxx is conductivity of the wire.
Since in total there is no current flow across the wire, we have
![]()
Substituting Eqs.(4.2),(4.3) into Eq.(4.4) gives
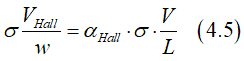
or
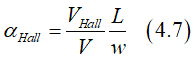
The Hall resistance RHall is defined as
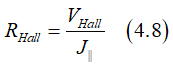
where J|| is the current flowing throw the nanowire
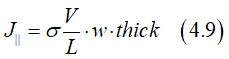
where thick is wire thickness
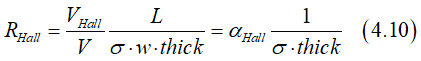
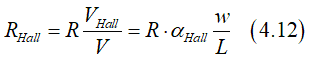
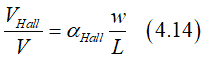
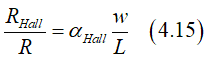
This case when metallic wire consists of two layers: The first layer is made of a ferromagnetic metal. The second layer is made of a non-magnetic metal. The Hall current is generated only inside ferromagnetic
The Hall current J⊥, which flows across wire, can be calculated as
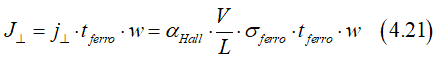
where j⊥ is the Hall current density , tferro is the thickness of ferromagnetic layer, w is the wire width, L is the wire length and V is the bias voltage. αHall is the Hall angle of the ferromagnetic metal. It is assumed that the Hall angle αHall=0 in the non-magnetic metal.
Due to the charge accumulation, the current flows in the opposite direction in both layers
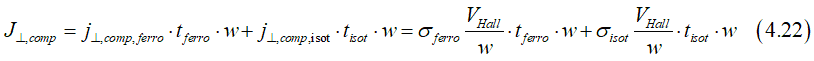
tisot is the thickness of layer of the non-magnetic metal, σferro,σisot are conductivities of ferromagnetic and non-magnetic metals..
Since in total there is no current flow across the wire, we have
![]()
Substituting Eqs. (4.21),(4.22) into Eq.(4.22a) we have
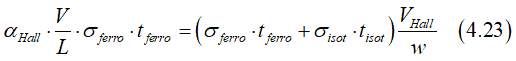
Simplifying Eq.(4.23) gives the Hall angle in case of wire consisted of two layers as
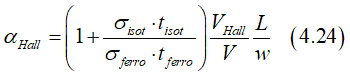
(fact): ![]() Even though the magnetization can be zero in an antiferromagnet or a compensated ferromagnet, the material still experiences a substantial Anomalous Hall effect (AHE)
Even though the magnetization can be zero in an antiferromagnet or a compensated ferromagnet, the material still experiences a substantial Anomalous Hall effect (AHE)
(reason 1: bulk contribution): ![]() (a different scattering probability of conduction electron for two magnetic lattices of opposite spins) The AHE occurs due to spin-dependent scattering of conduction electrons on localized d- and f- electrons. An antiferromagnet or a compensated ferromagnet usually consists of two magnetic lattices of two different materials, which are exchange- coupled antiferromagnetically and, therefore, are directed opposite to each other. If the spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other, there is no net magnetization. However, a spin-dependent scattering of a conduction electron depends on the material of the localized electron and , therefore, the scattering probability is different for localized electrons of each magnetic lattice. The scattering probability of a conduction electron is very different on two magnetic lattices, even though the total spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other. It is the reason why AHE exists in an antiferromagnet and a compensated ferromagnet.
(a different scattering probability of conduction electron for two magnetic lattices of opposite spins) The AHE occurs due to spin-dependent scattering of conduction electrons on localized d- and f- electrons. An antiferromagnet or a compensated ferromagnet usually consists of two magnetic lattices of two different materials, which are exchange- coupled antiferromagnetically and, therefore, are directed opposite to each other. If the spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other, there is no net magnetization. However, a spin-dependent scattering of a conduction electron depends on the material of the localized electron and , therefore, the scattering probability is different for localized electrons of each magnetic lattice. The scattering probability of a conduction electron is very different on two magnetic lattices, even though the total spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other. It is the reason why AHE exists in an antiferromagnet and a compensated ferromagnet.
(reason 2: interface contribution): ![]() (a different scattering probability across interface) Another substantial contribution to AHE is the spin-dependent scatterings across an interface.Again two magnetic lattices contribute very differently to the probability of such scattering. In total, the spin-dependent scattering probability is non-zero, even though the total spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other. It is an additional contribution to AHE in an antiferromagnet and a compensated ferromagnet.
(a different scattering probability across interface) Another substantial contribution to AHE is the spin-dependent scatterings across an interface.Again two magnetic lattices contribute very differently to the probability of such scattering. In total, the spin-dependent scattering probability is non-zero, even though the total spins of each magnetic lattice are equal to each other. It is an additional contribution to AHE in an antiferromagnet and a compensated ferromagnet.
compensated ferromagnet: FeTb |
|---|
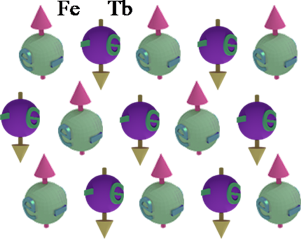 |
| Even though the net magnetization might be zero, AHE is very large in this material |
| The localized electrons of Fe and Tb have different p- and f- symmetries. The exchange interaction is strong for similar electrons and weak for electrons of different symmetries. As a result, there is a very strong ferromagnetic exchange interaction between identical d- electrons of Fe and identical f- electrons of Tb. However, the antiferromagnetic exchange interaction between Fe and Tb is weak, even though the distances Fe-Fe, Tb-Tb and Fe-Tb are nearly the same in an amorphous FeTb. |
The compensated ferromagnet like FeTb is a compound of two metals. Each metal has a different symmetry of the localized electron. For example, the symmetry of Fe electrons is the d- type and the symmetry of Tb electrons is the f- type. This material has two spin lattices. In each lattice all spins are aligned in one direction, There is a weak antiferromagnetic interaction between the Fe lattice and the Tb lattice. As a result, all spins of Tb electrons are opposite to the spins of Fe electrons. (See more details about exchange interaction here).
(fact) ![]() The exchange interaction is strong for similar electrons and weak for electrons of different symmetries.
The exchange interaction is strong for similar electrons and weak for electrons of different symmetries.
As a consequence, the ferromagnetic exchange interaction is strong between identical d- electrons of Fe and between identical f- electrons of Tb, but he antiferromagnetic exchange is weak between electrons of different symmetries: d- electrons of Fe and f- electrons of Tb, even though in an amorphous FeTb all distances Fe-Fe, Tb-Tb and Fe-Tb are the same.
(fact) ![]() Interaction between electrons of the same or similar spatial symmetry is larger than the interaction between electrons of a very different spatial symmetry.
Interaction between electrons of the same or similar spatial symmetry is larger than the interaction between electrons of a very different spatial symmetry.
As a consequence, the interaction (the scattering) between conduction electrons of the ps- symmetry and localized electrons of d- symmetry (e.g, electrons of Fe) is larger than the interaction (the scattering) between conduction electrons and localized electrons of f- symmetry (e.g, electrons of Tb).
As a consequence:
the interaction (the scattering) between conduction and d- electrons is strong  ; the interaction (the scattering) between conduction and f- electrons is weak
; the interaction (the scattering) between conduction and f- electrons is weak 
As a consequence: Main contribution to AHE is from d-electrons (electrons of Fe), but not from f-electrons (electrons of Tb)
Q. The spin Hall effect (SHE), anomalous Hall effect(AHE) and inverse spin Hall (ISHE) effect are very similar. How to distinguish between these effects?
A.
Q. Since all effects: SHE, AHE and ISHE are related to scatterings, does it mean that the spin Hall effect, anomalous Hall effect and inverse spin Hall effect can occur only in "bad" metals with a large number of defects?
A. The magnitude of these effects may be large only in case of metal having a sufficient number of defects. Therefore they can be observed easily in “ bad” metals with a small conductivity. For example, FeBTb, which conductivity is 50 times smaller than the conductivity of gold and 12 times smaller than the conductivity of monocrystal iron, has a large Hall angle (~0.5 deg).
In the case when the density of defect is very large, the electron wave function overlaps several defect simultaneously, it would make all side- jump scatterings spin-independent and they would not contribute to the spin Hall effect, and inverse spin Hall.
Other important condition for existence of spin-dependent side- jump scatterings is that the electron mean-free path should be shorter than the effective radius of electrical field around a defect.
Anomalous Hall effect
Q. For the anomalous Hall effect, is it essential for electron gas to be spin-polarized?
A.
Q. Why there are no anomalous Hall effect and no Inverse Spin Hall effect in case when the magnetization and spin polarization is in-plane and along the main current (along the wire)?
A. The spin polarization of electron gas is directed along an applied magnetic field. The defect induces an electric field around itself. An electron, which moves in this field, experiences the effective magnetic field of spin-orbit interaction , which is directed either up or down, when for electrons scattered into the left or right. Because of different directions of the effective magnetic field of the spin-orbit interaction, the probability of electron scattering toward left and right may be different and it this difference is the spin-dependent. In the case when the effective magnetic field is along the spin of electron, electron energy is larger. The energy difference for electrons with spin up and spin down is the reason for the spin-dependent scatterings.
When the magnetic field is applied along the wire, the spin direction of the spin-polarized electrons (electrons of TIA assembly) is along the wire as well. The electrons of this spin direction have the same energy in magnetic field directed up and down. Therefore, the effective magnetic field of the spin-orbit interaction, which is directed up and down, does not make scattering probabilities into the left and into the right to be different and scattering to be spin-dependent. This is the reason why there is no anomalous Hall effect when a magnetic field is applied along a wire.
types of the Hall effect |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| click on image to enlarge it. Zayets 2020.03 |
Q. The electrical field around defect is distributed in all directions. Why there is difference of scattering probabilities only between left and right directions as it is shown in above Fig.?
The scattering current may flow only if there is a difference in scattering probabilities into two opposite direction. The spin-orbit interaction makes this difference. The effective field of the spin-orbit interaction is directed up and down for electrons scattered into the left and into the right. Since the electrons with spin directed up and down have different energies in this field, their scattering probability is different. Similar, the electrons, which spin is directed left and right, have different scattering probabilities into up and down directions.
Q. In above Figure, spin-up electrons are scattered into the right and spin-down electrons are scattered into the left. Why not in opposite direction?
A. This direction is chosen as an example . In which direction electrons are scattered depends on a material. And specifically it depends whether the density of states in a metal increases or decreases with energy at the Fermi surface. When electron has been scattered, it experiences the electrical field at back side of the defect, which directed from front to back of the wire. This electrical field induces the effective magnetic field of the spin-orbit interaction, which is directed upward when the electron moves to the left (See here) and it is directed downward when the electron moves to the right. In the case when the effective magnetic field is along the spin of electron, electron energy is larger. When the density of states in a metal increases with increasing electron energy, the scattering probability is larger when electron spin is along the effective magnetic field. Therefore, the case shown in above Figure corresponds to a metal, in which the density of states decreases with energy.
Q. In Figure 1 hit it is only shown that only the electrons contribute into the effects. Is there any contribution of holes into the effects??
The holes (electrons of the energy lower than the Fermi energy) contributes nearly equally as the electrons (electrons of the energy higher than the Fermi energy). Importantly, the polarity of the hole and electron contributions are the same. This is the reason why the spin Hall effect, anomalous Hall effect and inverse spin Hall effect are effects with a large magnitude. It is similar to the case of the ordinary Hall effect
Reason why a scattering become spin-dependent |
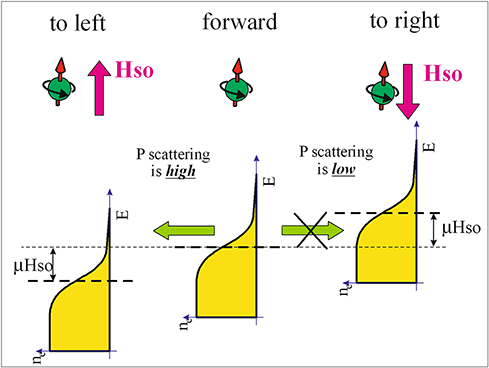 |
When a spin-up electron moves forward (central), its scattering probability is different towards left and towards right. The Fermi-Dirac electron distributions before scattering (center), after scattering to the left (left) and to the right (right) are shown in yellow. The vertical axis is the electron energy. The horizontal axis is the occupation probability. The electron energy depends on mutual directions of the electron spin and the effective field of the spin-orbit interaction Hso The scattering probability is highest, when at the energy of high occupation probability before scattering (center) there is sufficient number of unoccupied states after scattering (left or right). It is the case of scattering towards left. |
Notes:
When an electron is scattered on a defect, behind the defect the electrical field of the defect is directed along the electron movement. A moving electron experiences the effective magnetic field of the spin-orbit interaction only when electron moves across an electrical field.
When the electron is scattered towards left, the effective magnetic field of the spin-orbit interaction Hso is directed up and along the electron spin. Therefore, the energy the scattered electron becomes smaller.
When the electron is scattered towards right, the Hso is directed down and opposite to the electron spin. Therefore, the energy the scattered electron becomes larger.
As can be seen from Figure, for scattering towards left there are many unoccupied quantum states, therefore the scattering probability towards left is higher. In the contrast, there are almost no unoccupied quantum states for scatterings toward right, therefore the scattering probability towards right is lower.
Families of linear Hall effects. Influence of hysteresis loop |
||||||
|
||||||
Both the magnetization of the localized electrons and the magnetization of conduction electrons reverse its sign when the external magnetic field reversed. It makes the spM contribution independent on the polarity of the external magnetic field. |
||||||
| αHall,spM=8 mdeg; αAHE=20 mdeg; αISHE=4 mdeg; αOHE=1 mdeg/KG; sp0=70% ;Hpump= 1kG; | ||||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
It is a join contribution of spins of localized and conduction electrons
The Hall angle αHall,spM from this contribution is proportional to both the magnetization Md of localized electrons and the magnetization Mcond of conduction electrons
αHall,spM ~ Md · M cond
Since the magnetization Mcond of conduction electrons is proportional to the number of spin- polarized electrons and therefore to the spin polarization, αHall,spM is calculated as
αHall,spM ~ Md · sp
where sp is the spin polarization of the conduction electrons
![]() Except a few exceptions, the direction of the spin polarization (sp) of spin- polarized conduction electrons is along the spin direction of localized electrons (magnetization). As a result, αHall,spM (~ Md · sp) does not on direction of M and therefore does not have a hysteresis loop.
Except a few exceptions, the direction of the spin polarization (sp) of spin- polarized conduction electrons is along the spin direction of localized electrons (magnetization). As a result, αHall,spM (~ Md · sp) does not on direction of M and therefore does not have a hysteresis loop.
![]() In contrast to any other types of Hall effect, the spM- type Hall effect does not have a hysteresis loop.
In contrast to any other types of Hall effect, the spM- type Hall effect does not have a hysteresis loop.
αHall,spM is only slightly depends on an external magnetic field H due to the dependence of spin polarization sp on H



The polarity of the Hall voltage due to the hot electrons is usually opposite to that of the equilibrium electrons.
The conductivity of Fe and Co is hole-dominated. The conductivity of the hot electrons is the electron-type. Therefore, the polarity of the Hall voltage is different for these two types of conductivity.
The hot electrons can be excited in a metal or semiconductor by a light pulse or due to an electron current above a small tunnel barrier or contact barrier
Origins of Hall effects |
||||||||
|
A good theoretician can always fit its own theory to experimental data. It does not matter whether the model is correct or completely wrong |
|||||||
|
|||||||
click on image to enlarge it |
I am very surprised that any theoretical model for the origin of the AMR, which has been proposed for the last 70 years, always has a "perfect" fit with with the experimental data. From the present view it is clear that each of the proposed model describes either only one of many contributions to the AMR and/or to the ISHE or completely incorrect.
I am not surprised about the present time (2000- 2020), when there is a burst of a fake and "highlight" research and when publishing of "anything" in a research paper is possible. I am surprised about the time of 1960-1970, when the research was flourished and there were many excellent ideas, models and research results. Still every researcher had to show a "perfect" fit of theory and experiment, even in the cases when it was very clear that the full understanding of the effect is still far away. For example, Smit (1955), (1958) has described correctly the skew scattering mechanism and Berger (1970) has described correctly the side-jump scattering mechanism having a very poor and primitive tools. There were no computers. The understanding of the spin- orbit interaction was poor and primitive. Only mathematical method, they have used, was the minimization of Hamiltonian (which itself was not fully correct). It is not the best tool to study the features of the spin- dependent scatterings. Even the term "Inverse Spin Hall effect" did not exists at that time. Therefore, the Hall effect was not divided into the AHE and ISHE contributions. Still they have described correctly and precisely the main essence and the main tendencies of effects. They are very amazing and talented scientists!
There is no relation between AMR/PHE and AHE.
From an experiment, this fact is known for a while. See, for example, T.R. Mcguire and R.I. Potter, IEEE Trans. Magn. (1975).
From theory point of view, the AMR/PHE and AHE have different symmetries and different physical origins. Therefore, they are two very different effects.
Difference 1: difference in the symmetry
The AHE is a linear magneto-transport effect. The AMR/PHE is a second- order magneto-transport effect. In a nanomagnet there are 3 independent variables, which time-inverse symmetry is broken: (1) externally-applied magnetic field H; (2) the total spin Sd of localized d- electrons (or the magnetization M) and (3) the total spin Scond of the spin-polarized conduction electrons (or the spin polarization). A linear magneto-transport effect is linearly proportional either to H or Sd or Scond. The ordinary Hall effect is proportional to H. The AHE is linearly proportional to Sd. The inverse spin Hall effect (ISHE) is linearly proportional to Scond. A 2nd order magneto-transport effect is proportional to a product of a pair from H, Sd and Scond. Additionally to the AMR/PHE, the in-plane GMR is also a 2nd order magneto-transport effect.
Difference 2: difference in the physical origin.
The AHE is dependent only on the magnetization (Sd) and is independent of spin polarization of the conduction electrons (Scond). In contrast, the AMR/PHE depends on both the magnetization and the spin polarization. The origin of the AHE is the spin-dependent scatterings of conduction electrons, which depend on the spin of a d- electron, but is irrelevant to the spin of a conduction electrons. The origin of the AMR/PHE is also spin-dependent scatterings of conduction electrons, but of different type, which depend on the angle between spin of a d- electron and the spin of a conduction electron.
A 1st order magneto-transport effect (Anomalous Hall effect, Inverse Spin Hall effect & Ordinary Hall effect) can be easily distinguished experimentally from a 2nd order magento-transport effect (AMR/PHE, in-plane GMR etc.). Since the 1st order magneto-transport effect is linearly proportional to magnetization M + external magnetic field H, it reverses its polarity when H+M are reversed. In contrast, the 2nd order magento-transport effect is proportional to a square/product of magnetization M + external magnetic field H, it does not reverse its polarity when H+M are reversed.
It is a common rule for any magneto-transport measurement that two measurements are always done with the magnetization in the forward and reversed direction. Next, the symmetric and antisymmetric contributions of measurements are calculated. The anisymmerical contribution is associated with the 1st order magneto-transport effects and the symmerical contribution is associated with the 2st order magneto-transport effects. In this way any unwanted contribution of 1st order magneto-transport effects to a measurement of a 2st order magneto-transport effect can be avoided and vice versa.
As an example see my AMR/PHE measurement for nanomagnets here.
(about validity of the Barry Phase formalism) The formalism of the Barry Phase is valid and can be used only at a very low temperature (e.g. below 1K), when the electron mean free path (or the electron coherence length) is sufficiently long. For example, the formalism of the Barry Phase is useful for the description of the Quantum Hall effect and superconductivity. However, in the case of a metal or a semiconductor at T>1K the electron mean free path becomes shorter, the contribution of the spin-dependent scattering to AHE, ISHE, AMR/PHE dominates and the contributions related to a long mean free path are negligibly small. For example, at room T the mean-free path is about 1 nm-10 nm in a metal and about 10-100 nm in a semiconductor.
( about the importance of the scatterings for the charge and spin transport) The scatterings are a major engine mechanism, which creates transport itself (the superconductivity is an exception). There is no transport without scatterings (even in the case of coherent transport like tunneling) . It is no surprise that 90 % of transport properties are related to the scatterings. It is no surprise that properties of spin-related transports like AHE, ISHE, AMR/PHE are determined by features of the spin-dependent scatterings, which are the skew and side-jump scatterings.
(about sp-d interaction) The electron transport is determined by features of scatterings of the conduction electrons. The spin of localized- electron influences these scatterings.
A scattering of conduction electrons depends on the spin of the conduction electron. This spin-dependency of the scattering is the origin of the ISHE effect.
A scattering of conduction electrons depends on the spin of a localized electron. This spin-dependency of the scattering is the origin of the AHE effect.
A scattering of conduction electrons depends on the angle between spin directions of a localized electron and conduction electron. This spin-dependency of the scattering is the origin of the AMR/PHE effect.
(about influence of standing-wave electrons on AHE due to defects and interfaces )
![]() Due to defects and interfaces, a part of the conduction electrons becomes the standing-wave electrons. As a result, the conduction of metal decreases, but the strength of the AHE increases.
Due to defects and interfaces, a part of the conduction electrons becomes the standing-wave electrons. As a result, the conduction of metal decreases, but the strength of the AHE increases.
![]() (from Szymon Królak) you frequently mention, that there exist two currents: the current of full-filled states, as well as half-filled ones. However, during the explanation of the Hall effect, you state, that the full-filled states form standing waves and therefore do not move. Could you elaborate on that? I am referring to the explanation below, figure 15: The current of "full" states is the normal current. This means that the negatively charged "full" states diffuse from a "-" source toward a "+" drain. Due to the Hall effect, they should turn to the left (similar to the electrons shown in Fig. 14). However, most of the electrons, which occupy the "full" states, are the standing-wave electron. (See Fig.9 here). The standing-wave electrons do not move, therefore they do not contribute to the Hall current
(from Szymon Królak) you frequently mention, that there exist two currents: the current of full-filled states, as well as half-filled ones. However, during the explanation of the Hall effect, you state, that the full-filled states form standing waves and therefore do not move. Could you elaborate on that? I am referring to the explanation below, figure 15: The current of "full" states is the normal current. This means that the negatively charged "full" states diffuse from a "-" source toward a "+" drain. Due to the Hall effect, they should turn to the left (similar to the electrons shown in Fig. 14). However, most of the electrons, which occupy the "full" states, are the standing-wave electron. (See Fig.9 here). The standing-wave electrons do not move, therefore they do not contribute to the Hall current
![]() You are correct.
You are correct.
(about full state and standing- wave electrons): The full state and the sdanding-wave electrons are two different states of an electron. The full state is related to the electron spin and the standing- wave electrons are related to the electron wave vector.
(standing-wave electrons & their influence on the Hall effect)
(What is the electron current?) The electron current does not mean that the electron starts to move in one direction under applied voltage from "-" to "+" potential or the electron speed in this direction is changed. Even in absence of the applied voltage, there are always electrons, which move in both the forward and the backward directions. An electron current means that there are more electrons, which are moving along applied voltage, than electrons, which are moving in the opposite direction.
In absence of the voltage the number of electrons moving in any direction is exactly equal to the number of electrons moving in the opposite direction. The applied voltage makes a number of electrons moving in each direction different. In the direction along the applied voltage the number becomes slightly larger and in the opposite direction the number becomes slightly smaller.
(Origin of the standing wave electrons): Next, just imagine, that there are two defects close to each other inside a metal, which reflects the electron backward as a mirror reflects light. Then, the electron bounces between these two defects forward and backward. Such a bounced electron is a sum of forward and backward-moving electrons with exactly the same amplitude of the wave function. It means that the existence of these two defects firmly fixes the ratio between numbers of forward and backward-moving electrons and the applied voltage does not change this ratio and the numbers of the forward and backward-moving electrons are always equal independently of the applied voltage. Since the applied voltage does not change the ratio between the numbers of the forward- and backward- moving of these electrons, these electrons do not contribute to the electron current. These electrons, I call the standing-wave electrons.
In the above example, I assumed that the reflection of an electron from a defect is 100 %. In reality the reflection is much smaller. It is smaller than 1 %. As a result, only a small part of the conduction electrons are the standing- wave electrons, for which the ratio of is fixed and which do not contribute to the electron current. For other conduction the ratio is not fixed and they do contribute to the electron current.
(an interface as the origin of the standing-wave electrons): A surface or an interface between two metals substantially reflects the conduction electrons. As a result, there are many standing-wave electrons in the proximity of the interface and the conductivity near an interface is smaller than the conductivity in the bulk of the metal. Additionally, the conductivity near an interface is anisotropic, because the reflection of an electron from the interface depends on the electron incident angle.
![]() (Why should we care about the standing- wave electrons and why the standing-wave electrons are important for AHE and ISHE?) The standing- wave electrons do not contribute to electron current, so what? Why we just cannot forget about them? The localized electrons do not contribute to current as well.
(Why should we care about the standing- wave electrons and why the standing-wave electrons are important for AHE and ISHE?) The standing- wave electrons do not contribute to electron current, so what? Why we just cannot forget about them? The localized electrons do not contribute to current as well.
There are two reasons:
The 1st reason is that there is another kind of the electron current, for which an electron just jumps from one spatial position to another. It is a very inefficient current and usually can be ignored, but when the number of standing wave electrons becomes larger, the contribution from this 2nd-type of current can become dominated. This kind of current has a huge AHE. Therefore, when the number of standing-wave electrons becomes larger, the normal current decreases and the 2nd type of current increases, AHE becomes huge. For example, the side-jump scatterings and the spin-dependent scatterings across the interface belong to this 2nd kind of current.
The 2nd reason, why the standing-wave electrons are important for AHE, is that a standing-wave electron effectively couples the conduction and localized electrons.
(localized vs conduction electrons)The localized and the conduction electrons are very different. Their size, symmetry and properties are very different. For example, the spin distributions of localized and conduction electrons are very different. The spins of localized electrons are either parallel or antiparallel to each other. There are 3 groups of conductions electrons with respect to the spin: spin-polarized, spin-unpolarized and spin-inactive conduction electrons (or full state). The different frequency of the scatterings makes the properties of conduction and localized electrons to be so different.
(difference in scattering probability) The scatterings of the conduction electrons are frequent and the scatterings of localized electrons are very rare. The scatterings between localized and conduction electrons are very rare as well, because of the difference in size and symmetry of these different types of electrons. Additionally, a conduction electron moves, a localized electron stays at one place. Therefore, there is a difference in momentum.
The standing-wave electrons have the same symmetry and the same size as the moving conduction electrons, but they stay at the same place. As a result, both types of scatterings between localized and standing- wave electrons and standing- wave and moving conduction electrons are relatively frequent. Overall, the existence of standing-wave electrons makes the probability of scattering between the localized and standing- wave electrons higher.
Since AHE is originated from a spin- dependent scattering of conduction electrons on the localized electrons, the high scattering probability between the conduction and localized electrons makes AHE larger.
(About "full" states or spin-inactive states)
A conduction electron also can be distinguished by its spin. There are 3 different groups of conduction electrons, which are distinguished by the spin.
(group 1) “Full” state or spin- inactive state. It is the case when two electrons occupy one quantum state. The time-inverse-symmetry for this state is not broken. The spin direction of each individual electron cannot be distinguished in this state. As a result, such electrons do not contribute to any spin- related features.
(group 2) Spin- polarized electrons. It is the case when one electron occupies one quantum state and one state remains unoccupied. The spins of all electrons are directed in one direction.
(group3) Spin- unpolarized electrons. It is the case when one electron occupies one quantum state and one state remains unoccupied (similar to group 2). The spins are distributed equally in all directions. Each group has its own distribution of electrons over the electron energy. Since the electron distribution mainly determines features of the electron current, the electron current for each group is very different.
The electrons of each group could be either the standing- wave conduction electrons or “normal” moving conduction electrons.
(increase of standing wave electrons at a lower energy. The hole transport)
![]() (following question from Szymon Królak) Why most full-state electrons are standing-wave electrons? In the explanation above, you stated that a single defect can localize an electron. Are most of the full-state electrons standing-wave electrons because of the fact that at energies lower than the Fermi energy there are a lot of electrons and the Pauli pressure is large? In short: is the effect of a large amount of neighboring full-state electrons similar to a defect, in the sense that it can localize an electron?
(following question from Szymon Królak) Why most full-state electrons are standing-wave electrons? In the explanation above, you stated that a single defect can localize an electron. Are most of the full-state electrons standing-wave electrons because of the fact that at energies lower than the Fermi energy there are a lot of electrons and the Pauli pressure is large? In short: is the effect of a large amount of neighboring full-state electrons similar to a defect, in the sense that it can localize an electron?
![]() You understand the case correctly. Even though the full state is a property of the spin and the standing-wave electrons are a special property of electrons, at an electron energy substantially lower than the Fermi level nearly all electrons are in the full-state or the spin-inactive and are the standing wave electrons.
You understand the case correctly. Even though the full state is a property of the spin and the standing-wave electrons are a special property of electrons, at an electron energy substantially lower than the Fermi level nearly all electrons are in the full-state or the spin-inactive and are the standing wave electrons.
At an energy substantially lower than the Fermi level, almost all states are filled by two electrons and there are only a few, which are filled by one electron and which one space is not filled. The states filled by two electrons are "full" states or spin inactive states. The states filled by one electron are holes.
When there are a few empty states, the scattering of an electron from a "full" state into the empty space becomes rare. For this reason, the life time of the "full" state becomes long (e.g. in comparison to the life time of the "full" state at the Fermi energy) and, consequently, the length of the "full" state (or the same the propagation length between two scatterings) becomes longer. For a longer length the reflection from defects and interfaces becomes more probable and, therefore, there are more standing-wave electrons. It is because one electron covers many defects and interfaces simultaneously.
By the way, the standing-wave electrons are not a "defect" electrons, because an interface is more effective in creation of a standing-wave electron than a defect due to its better reflection of an electron.
(standing-wave electron vs localized electron) The standing-wave electron is not a localized electron. The localized electron is an electron of the size of an atomic orbital of ~0.1 nm. In Fe or Co the localized electron has the d- symmetry. The scatterings of the localized electrons are rare. The standing-wave electron is a conduction electron of a longer size of about 10-100 nm. The symmetry of the standing-wave electron is the symmetry of the conduction electrons (p- or s-). The scattering of the standing-wave electron is frequent.
(timescale of AHE; AHE in picosecond timescale)
![]() (from Chen Xiao) What about the timescale of AHE? People use ISHE to generate THz electrical field, which indicates that ISHE is in the sub-picosecond range or shorter. The magneto-optical effects such as KERR or FARADAY rotation have been popular techniques to probe magnetism. The timescale of MO effects might be a few femtoseconds. Would it be possible to detect the AHE in the dynamical regime? (It is noticed that G. Sala et al. achieve a time- resolved hall-effect detection in the nanosecond range.)
(from Chen Xiao) What about the timescale of AHE? People use ISHE to generate THz electrical field, which indicates that ISHE is in the sub-picosecond range or shorter. The magneto-optical effects such as KERR or FARADAY rotation have been popular techniques to probe magnetism. The timescale of MO effects might be a few femtoseconds. Would it be possible to detect the AHE in the dynamical regime? (It is noticed that G. Sala et al. achieve a time- resolved hall-effect detection in the nanosecond range.)
![]() The timescale of AHE is not very fast. AHE relaxation time is moderate.
The timescale of AHE is not very fast. AHE relaxation time is moderate.
(reason 1: the time to chage distribution function) The AHE, ISHE or any other transport effect cannot be very fast, because any transport effect is related to a change of the electron distribution function and such a change cannot be very fast. In order to reach an equilibrium or a quasi- equilibrium distribution, the electron should experience many scatterings and it takes a time.
(reason 2: the time to accamulate charge on sides of a metalic wire) the timescale of AHE depends on the sample geometry. The longer timescale is not only because of the timing taking to establish the equilibrium distribution function, but also because the time required to redistribute the charge.
The steps to establish an equilibrium AHE are:
(step 1) After the bias electron current is on, the perpendicular-to-bias current starts to flow due to the spin-dependent scatterings.
(step 2) The charge is accumulated at the boundaries of the nanowire due to the perpendicular-to-bias current.
(step 3) The current flows opposite to the perpendicular-to-bias current due to the AHE voltage created by the charge accumulation.
(step 4) The current due to the charge accumulation increases until it fully balances the perpendicular-to-bias current. The currents, the accumulated charge and AHE voltage are larger for a wider nanowire.
(note) Even though the conventional measurement of AHE is a measurement of accumulated charge at sides of a metallic wire (the Hall voltage), it might be a method to measure directly the perpendicular- to- wire current due to AHE instead of the accumulated charge. In this case, the AHE is faster and independent of the sample geometry.
(reason 3: the timing of the spin-dependent scatterings)) the origin of AHE is spin-dependent scattering of the conduction electrons (skew scattering, side- jump scattering, scatterings across interface). The timescale of AHE cannot be shorter than the timescale of the spin- dependent scatterings.
![]() ( fast non-equilibrium effects: hot electrons)
( fast non-equilibrium effects: hot electrons)
There are faster effects, which do not require an establishment of a thermal equilibrium. For example, a current of the hot electrons.Even though the properties of such non-equilibrium effects are different from their equilibrium cousins, there are many similarities between both effects. The timescale of AHE due to the hot electrons is still limited by the reason 2 and reason 3.
![]() ( saturation velocity: the fastest speed of the electrons in a solid)
( saturation velocity: the fastest speed of the electrons in a solid)
The moving speed of even the hot electrons is not infinite and, in fact, it is moderate. The moving speed is limited by the saturation velocity of the electron in a solid, which equals to ~75 um/ns. For example, even at the fastest speed of the hot electrons (or of any electrons) it takes 80 ps in order for the hot electrons to pass 6 micrometers. It limits the timescale of the Hall effect. I have measured the saturation velocity (See here). The origin of the saturation velocity is that near the saturation velocity the electrons lose their energy to photons very fast similarity as an airplane flies close to a breaking of the sound barrier.
 ( correct definition of the photoinduced Hall effects)
( correct definition of the photoinduced Hall effects)
Many researchers name any photoinduced Hall effect as the Anomalous Hall effect (AHE). It is incorrect. There is a family of the Hall effects (See here). Each type of the Hall effect is distinguished according to its origin.
Types of photoinduced Hall effect:
(type 1) photoinduced Anomalous Hall effect (AHE). It is the case when light changes the number of the localized d- electrons. It can occur only in a ferromagnetic metal.
(type 2) photoinduced Inverse spin Hall effect (ISHE). It is the case when light changes the number of the spin-polarized conduction electrons. It is the most common photoinduced Hall effect. See my description of the photoinduced ISHE here.
(type 3) photoinduced Planar Hall effect (PHE) or, the same, the photoinduced Anomalous Magnetoresistance (AMR). It is the case when light changes either the number of the spin-polarized conduction electrons or the number of the localized d- electrons, which affects the probability of spin-dependent scatterings of a spin-polarized conduction electron on a localized d-electron. The symmetry of the photoinduced AMR/PHE effect is different from the symmetry of AHE and ISHE.
(type 4) photoinduced Ordinary Hall effect (PHE). It is the case when light changes or creates the internal magnetic field in a material, which is not related to a change of the number of the spin-polarized conduction electrons or the number of the localized d- electrons.
 (about timescale of the Kerr and Faraday effects)
(about timescale of the Kerr and Faraday effects)
According to the classical Quantum Mechanic any Magneto-optical effect (Faraday, Kerr and MCD effects) has no timescale. They are infinitely fast. The Faraday, Kerr and MCD effects all originate from a Zeeman splitting of the energy level in a magnetic field. The energy level and the Zeeman splitting exists primarily of any dynamics. Therefore, it is meaningless to assign any dynamics to the energy level.
Of course, a change of some external parameter may change the strength of the magneto-optical (MO) effect. However, the effect timescale is determined by the timescale of the external parameter, but not by the timescale of MO effect. For example, the MO strength depends on the strength of the external or internal magnetic field, under a change of the magnetic field the MO strength changes. The timescale of this process is determined only by the timescale of the change of the magnetic field. The timescaly of MO effect itself is instant.
Another example is a filling of one of Zeeman-split energy levels by the spin- polarized electrons. This event also changes the MO strength. Similarly, only the speed of the filling or emptying of the energy level determines the timescale in this case.
Also, there is a timescale of the optically- induced electron transition from one level to another. This timescale is very short and equals to a half of the period of a Rabi oscillation.
![]() (following question from Chen Xiao) The response speed of AHE is limited by the distance and path that hot electrons travel, while the MO effect is supposed to be "real-time". The charge is accumulated to build the electric field, in which another current flows antiparallel with its counterpart. The PN-junction and ferromagnetic nanowire (or ferromagnetic "gate") have something in common. Very interesting! It's possible to make time-resolved measurements of this non-equilibrium effect and to detect the ferromagnetic state by electrical methods. Roughly, I have had a picture of how the AHE voltage is generated and to be read through your clear description.
(following question from Chen Xiao) The response speed of AHE is limited by the distance and path that hot electrons travel, while the MO effect is supposed to be "real-time". The charge is accumulated to build the electric field, in which another current flows antiparallel with its counterpart. The PN-junction and ferromagnetic nanowire (or ferromagnetic "gate") have something in common. Very interesting! It's possible to make time-resolved measurements of this non-equilibrium effect and to detect the ferromagnetic state by electrical methods. Roughly, I have had a picture of how the AHE voltage is generated and to be read through your clear description.
(about rotation of an electron around a nucleus)
![]() (from Ekta Yadav) "A conduction electron rotates around each nucleus. " Can you give me some reference for this statement?
(from Ekta Yadav) "A conduction electron rotates around each nucleus. " Can you give me some reference for this statement?
yes, the electron does rotate around a nucleus. Literally. It is not a rotation when one dot is rotating around another dot. For example, as the Earth is rotating (orbiting) around the Sun. The rotation of an electron around a nucleus is more complex, because the electron is a wave. Nevertheless, it is as a real rotation as any rotation could possibly be.
(Rotation in Quantum mechanics. Rotation & electron orbital) In order to understand it, it is better to start from a 1D structure. Let us look at a wave, which is reflected back and forward between two mirrors. This quantum state is static. It does not move in space.. The field distribution is static as well. However, there are waves, which move forward and backward. Next,Let us look at a similar 2D structure. A wave can move around a circle. In this case, the quantum state has a positive and negative orbital moment for a clockwise and counterclockwise rotation, respectively. Additionally, a quantum state may have zero orbital moment. In this case, the state consists of two waves moving or rotating in the opposite directions. This 2d case is similar to the 1D case of a wave reflecting between mirrors. In the 3D case, the electron rotation can be along any 3D vector (x,y,z). Correspondingly, the direction of the orbital moment can be along any 3D vector (x,y,z).
(Rotation & Orbital symmetry) The fact of rotation of the electron around the nucleus has an even more fundamental origin. In nature, all conserved parameters of an object have corresponding broken symmetries. The spin describes the broken time-inverse symmetry. The rotation (as well as the orbital moment) describes more complex breaking of the symmetry. The rotation means breaking of the space symmetry along with breaking of the time- inverse symmetry. The electron of an atom orbital breaks just this specific symmetry corresponding to the rotation. Meaning that, judging from the most fundamental definition of the rotation, the electron of an atomic orbital is truly rotating around the nucleus.
(Rotation & Bonding between neighbor atoms) The electron rotation or, the same, the electron having a non-zero orbital moment also means that the spatial distribution of the electron wavefunction is changing in time. When an electron state participates in a bonding between atoms, the spatial distribution of the electron wavefunction is fixed, cannot change in time and, therefore, cannot be rotated. For this reason, the electron moment is quenched meaning the orbital moment is zero and there is no electron rotation around the nucleus (See here).
( difference between conduction and localized electrons)
![]() (from Prem) Which electrons works here as a conducting electrons and which are the localized d shell electrons? How can we differentiate both the electrons from each other because all electrons gona be same
(from Prem) Which electrons works here as a conducting electrons and which are the localized d shell electrons? How can we differentiate both the electrons from each other because all electrons gona be same
The localized and the conduction electrons are very very different.
(electron transport) Only the conduction electrons participate in the electron transport, the localized electrons do not. Therefore, the properties of the conduction electrons is all that matters for any electron transport effect like AHE.
(spatial symmetry:) Mostly, the conduction electrons have the s- or p- types of the spatial symmetry and the localized electrons have d- or f- types of the spatial symmetry. Additionally, the conduction electrons have a small d- symmetry component and the localized electrons have a p-symmetry component. The spatial symmetry is not a key feature, which makes the difference between the conduction and localized electrons.
The key feature, which distinguishes between the conduction and localized electrons, is the frequency of the electron scatterings. The scatterings of the conduction electrons are very frequent. At room T, a scattering occurs about each 10- 100 fs (10E-14-10E-13 s). Within such a short time between two scattering, a conduction electron has no time to react on external forces and fields and the properties of the conduction electrons is defined by the collective statistics. The reason why the scatterings for the conduction electrons are so frequent is the large size of the conduction electrons. The size of a conduction electron, which is equal to the mean-free path, is about 10-100 nm and there are billions of conduction electrons, which substantially overlap each other at any spatial point. This makes the scattering probability between a pair of conduction electrons very large.
In contrast, the size of a localized electron is very small, about 0.1 nm, which is about the size of an atomic orbital. A localized electron only slightly overlaps with a few close-nearbour localized electrons. As a result, the scattering probability of a localized electron is very small. It is scattered once per 1 us or even per 1ms. It is nearly the same as no scattering.
![]() Why does the frequency of the scatterings make such a large difference?
Why does the frequency of the scatterings make such a large difference?
The difference of the frequency of scatterings makes some properties of the conduction and localized electrons look the opposite. Some examples:
Spin distribution:
(localized electrons) along or opposite to a magnetic field (spin-up and spin-down distribution). The spin of a localized electron has more than enough time to align itself along the magnetic field.
(conduction electrons): group of spin-polarized electrons, for which all spins are aligned in one direction, and group of spin-unpolarized electrons, for which spins are equally distributed in all directions. The spin of a conduction electron has absolutely no time to align itself before scattering. The scatterings always mix up the spins of the conduction electrons. Only the total or average spin over all conduction electrons in the electron gas is conserved during these frequent scatterings. (See here and here)
Orbital moment:
(localized electrons): It is quenched. It means that the orbital moment of a localized electron is zero. It is because of the bonding of the localized electron to its few neighboring localized electrons. (See here)
(conduction electrons) It is unquenched.. It means that the orbital moment of a conduction electron can be non- zero (the same as in an atom). It is because the size of the conduction electrons is large, it simultaneously interacts with many other electrons and it is not bond to any specific direction.
I will try to answer your questions as soon as possible