Dr. Vadym Zayets
v.zayets(at)gmail.com
My Research and Inventions
click here to see all content |

Dr. Vadym Zayetsv.zayets(at)gmail.com |
|
 |
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
|
Heating of a ferromagnet. Curie–Weiss law. Curie Temperature Spin and Charge TransportAbstract:The heat affects both localized d-electrons and conduction electrons. The localized electrons starts to vibrate or swing with respect to each other. At room temperature, the average swing angle with respect to magnetic easy axis is about 15 degrees. The heat affects the conduction electrons very differently. All spins of the spin- polarized conduction electrons remains perfectly aligned along the easy axis under the heating. Due to the heating the number of spin- polarized conduction electrons decreases and the number of spin- unpolarized conduction electrons increases.
|
Heating of conduction electrons |
|---|
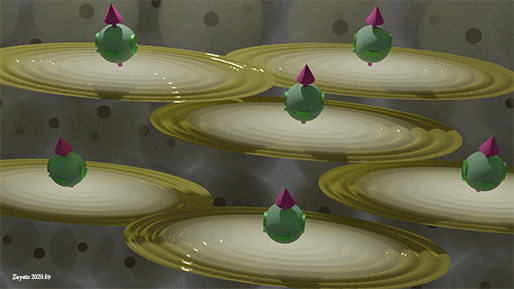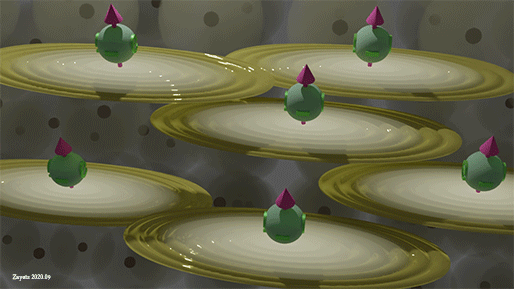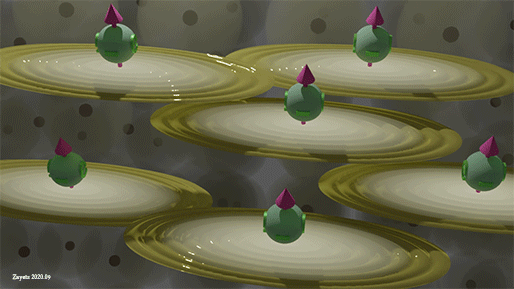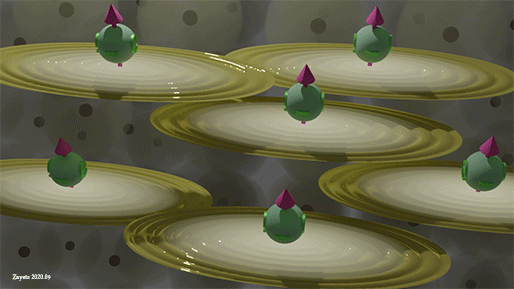 |
| Spins of all spin-polarized conduction electrons. Yellow ellipse shows the wave function of conduction electrons, green ball shows the spin directions. Background balls are the atomic orbitals |
| Spins of all spin-polarized conduction electrons are perfectly aligned along one direction |
| click on image to enlarge it |
All conduction electrons can be divided into two groups: (1) group of spin- polarized electrons and (2) group of spin- unpolarized electrons. In the group of spin-polarized electrons, all spin are directed precisely in one direction. In the group of the spin- unpolarized electrons, the spins are equally distributed in all directions.
 Why the effect of heating is so different for conduction and localized d- electrons
Why the effect of heating is so different for conduction and localized d- electrons 
Heating of localized d-electrons |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
(reason 1. Why)  Frequency of scatterings
Frequency of scatterings
conduction electrons:![]() scatterings are very frequent. About each 100 fs (10
scatterings are very frequent. About each 100 fs (10


 Langevin's Formulae.
Langevin's Formulae. Saturation of total magnetic moment (total spin) of a paramagnet in a large external magnetic field |
|---|
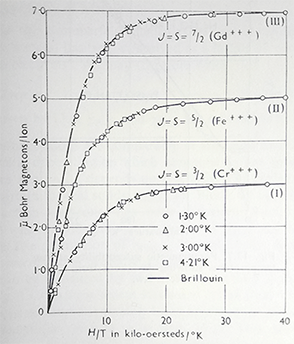 |
| Magnetic moment as a function of a ratio of magnetic to thermal energy H/T measured . in a large external magnet field H at low temperature T. Data for paramagnetic compounds: (I) potassium chromium alum; (II) feric ammonium alum; (III) gadolinium sulfide octahydrate. |
(note) |
|
| click on image to enlarge it |

effective magnetization M at room temperature |
|---|
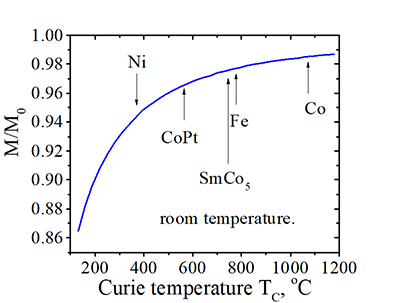 |
The effective magnetization at room temperature as a function of material Curie tmperature.M0 is saturation magnetization |
| (note): The magnetization decreases only a few percent at room temperature for the most of ferromagnetic metals. |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Curie-Weiss law |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
 Comparison of magnetic and thermal energies
Comparison of magnetic and thermal energies
Effective magnetic field of exchange interaction Hexchange |
|---|
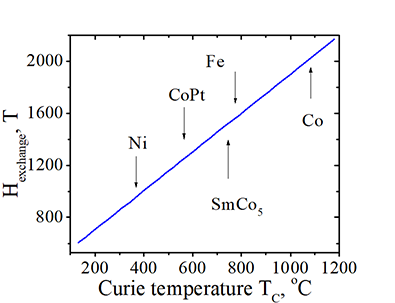 |
The effective magnetic field Hexchange of the exchange interaction, which an electron experiences from all neighbor electrons vs. material Curie temperature. |
(fact) At Tc the thermal fluctuations breaks exchange alignment of neighbor electrons. Therefore, the electron thermal energy becomes larger than the energy of the exchange interaction. |
| click on image to enlarge it |
(thermal energy) 
Increase of temperature per 1 degree increases the thermal energy per a particle on k ·1K= 1.38×10-23 J
k is the Boltzmann constant equals to 1.38×10-23 J/K.
(magnetic energy) ![]()
![]()
![]()
Applying magnetic field H of 1T (=104 Gauss) to an electron with spin increase its magnetic energy on H·μB=0.93 ×10-23 J
μB is Bohr magneton equals to 9.27 ×10-24 J/T

Applying 1 T of magnetic field increases the electron magnetic energy on the same increase amount of the electron thermal energy when temperature increases on 0.67 degrees
The exchange interaction aligns spins of neighbor atoms in a ferromagnetic material. In contrast, thermal fluctuations disaligns the spins. The Curie temperature Tc is the temperature until which there is neighbor - neighbor alignment in ferromagnetic material. At there is a balance between the energy of the exchange interaction and the thermal energy. From this balance condition the exchange energy and the effective magnetic field Hexchange of the exchange interaction are calculated.
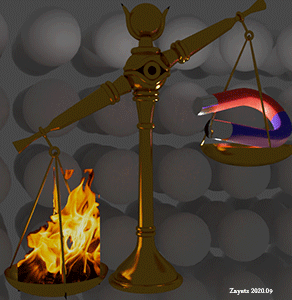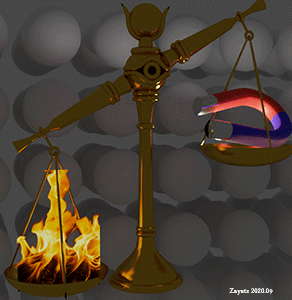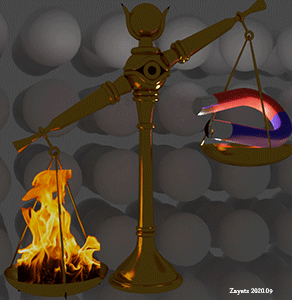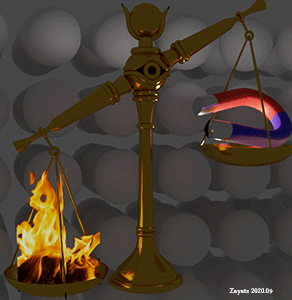
Magnetic field vs. thermal fluctuation. Localized d- electrons. Heating overweights magnetic field. |
|---|
 |
|
|
| (note) Applying an external magnetic field of 1 Tesla (10 kGauss) increases the energy of a localized d- electron similarly as the increase of temperature of 0.67 K. |
| click on image to enlarge it |
 (Spin waves)
(Spin waves) Why localized d- electrons support a spin wave, but conduction electrons do not????
Why localized d- electrons support a spin wave, but conduction electrons do not???? 
Spin Waves |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
Red arrows shows spin direction of localized d- electrons. The exchange interaction forces neighbor spins to be aligned to each other. |
||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
Reasons why conduction electrons cannot support a spin wave
(reason 1): ![]() frequent scatterings of conduction electrons
frequent scatterings of conduction electrons
The spin wave
(reason 2): ![]() large size of a conduction electron
large size of a conduction electron
The spin wave
(reason 3): ![]() fast movement of a conduction electrons
fast movement of a conduction electrons
The spin wave
(reason 4): ![]() weak exchange interaction between conduction electrons
weak exchange interaction between conduction electrons
The spin wave
Increase of Curie temperature under external magnetic field |
|---|
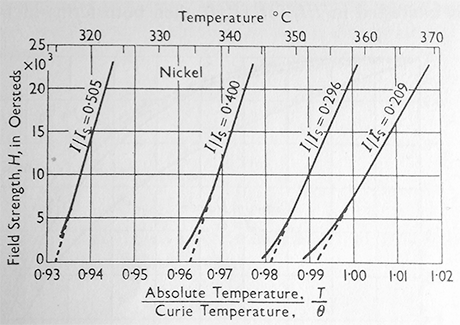 |
|
| click on image to enlarge it |
(note) Applying an external magnetic field of 1 Tesla (10 kGauss) increases the energy of a localized d- electron similarly as the increase of temperature of 0.5 K.
Magnetic field vs. thermal fluctuation. Localized conduction electrons. Magnetic field overweights Heating. |
|---|
 |
|
|
| click on image to enlarge it |
![]()
![]() I am strongly against a fake and "highlight" research
I am strongly against a fake and "highlight" research ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
I will try to answer your questions as soon as possible