Dr. Vadym Zayets
v.zayets(at)gmail.com
My Research and Inventions
click here to see all content |

Dr. Vadym Zayetsv.zayets(at)gmail.com |
|
 |
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
more Chapters on this topic:IntroductionTransport Eqs.Spin Proximity/ Spin InjectionSpin DetectionBoltzmann Eqs.Band currentScattering currentMean-free pathCurrent near InterfaceOrdinary Hall effectAnomalous Hall effect, AMR effectSpin-Orbit interactionSpin Hall effectNon-local Spin DetectionLandau -Lifshitz equationExchange interactionsp-d exchange interactionCoercive fieldPerpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)Voltage- controlled magnetism (VCMA effect)All-metal transistorSpin-orbit torque (SO torque)What is a hole?spin polarizationCharge accumulationMgO-based MTJMagneto-opticsSpin vs Orbital momentWhat is the Spin?model comparisonQuestions & AnswersEB nanotechnologyReticle 11
|
Volt 50B (Ta(3)/ FeB(1.1)/ MgO(7)/ W(1)/ Ru(5))
Measurement of magnetic and magneto- transport properties of nanomagnets. Measurement data.Abstract:High- precision, high- reproducibility, high- repeatability measurement of magnetic and magneto- transport properties of ferromagnetic nanomagnets using the Hall effectHigh-precision measurement of effect of spin-orbit torque (SOT effect): Dependence of magnetic and magneto- transport properties on electrical currentHigh-precision measurement of effect of voltage-controlled magnetic anisotropy (VCMA effect): Dependence of magnetic and magneto- transport properties on a gate voltage
|
Nanowire with two Hall probes |
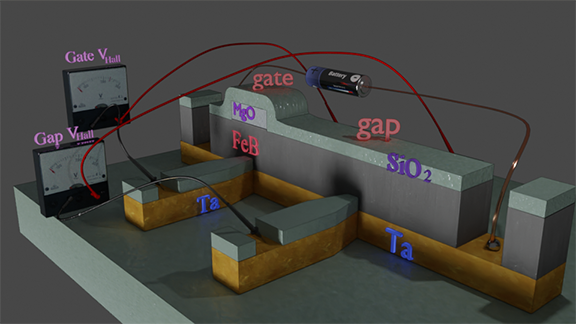 |
Measured hysteresis loop (See below) for gap regions indicates that the etching was stopped at MgO/FeB boundary |
| click on image to enlarge it |
(1.2) Spin-orbit torque: Measurement of dependence of Hall angle, Anomalous Hall effect (AHE), Inverse Spin Hall effect on current magnitude and polarity.
(measurement 2) ![]() Measurement of anisotropy field vs external perpendicular magnetic field
Measurement of anisotropy field vs external perpendicular magnetic field
(2.1) Measurement of PMA & Anisotropy field
(2.2) Spin-orbit torque: ""Field- like torque" ""Damp- like torque". Measurement of dependence of PMA on the electrical current .
(measurement 3) ![]() Measurement of magnetization switching under external perpendicular magnetic field
Measurement of magnetization switching under external perpendicular magnetic field
(3.1) Measurement of coercive field HC, retention time, size of nucleation domain, parameter delta Δ
(3.2) Spin-orbit torque: Current dependence of magnetization switching parameters.
Hysteresis loop |
||||
|
||||
Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
||||
| click on image to enlarge it |
Raw data Volt50.zip (.dat files and origin 9 files)
Conductivity: 0.039-0.62 S/m2
Anisotropy field Hanis =5kGauss
Coercive field = 170 Oe-220 Oe;
Hall angle measured=450- 800 mdeg
Intrinsic Hall angle of FeB= 1677- 2982 mdeg;
Gap region etched: stopped at MgO/ FeB interface
![]()
![]() magnetization- switching parameters:
magnetization- switching parameters: ![]()
![]()
Kerr Rotation angle MOKE |
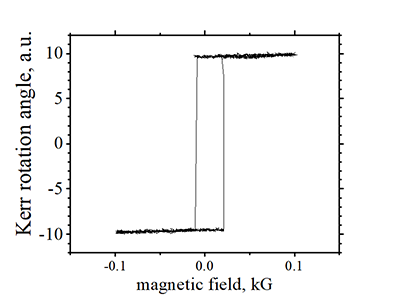 |
data of a plain film before nanofabrication |
| (note) Coercive field and shape of coercive loop is very different for a nanomagnet and film, from which it was fabricated, because of different magnetization switching mechanisms (See here) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
retention time τret
(gate): free35-> 1016 s; free36-> 106 s; free56-> 106 s; free82-> 1016 s;
(gap): free35-> 107 s; free36-> 1014 s; free56-> 108 s; free82-> 1010 s;
size of nucleation domain:
(gate): free35-> 55 nm; free36-> 35 nm; free56-> 30 nm; free82-> 55 nm;
(gap): free35-> 38 nm; free36-> 50 nm; free56-> 35 nm; free82-> 40 nm;
coercive field Hc:
(gate): free35-> 180 Oe; free36-> 205 Oe; free56-> 220 Oe; free82-> 175 Oe;
(gap): free35-> 180 Oe; free36-> 220 Oe; free56-> 200 Oe; free82-> 145 Oe;
parameter Δ :
(gate): free35-> 240; free36-> 100; free56-> 60; free82->240;
(gap): free35-> 110; free36-> 190; free56-> 150; free82->170;
(free 36): wire width: 200 nm; nanomagnet length: 100 nm; σ = 0.0446 S/m2
(free 35): wire width: 100 nm; nanomagnet length: 100 nm; σ = 0.039 S/m2
(free 56): wire width: 200 nm; nanomagnet length: 100 nm; σ = 0.049 S/m2
(free 82): wire width: 200 nm; nanomagnet length: 200 nm; σ = 0.063 S/m2
Since the nanowire is double- layer, which consists of Ta and FeB layer, the Hall angle αHall, FeB in FeB can be calculated from measured Hall angle αHall, measured (See here) as
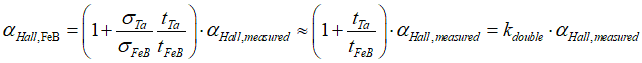
where 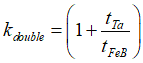
tFeB, tTa, σFeB,σTa are thicknesses and conductivities of FeB and Ta metals.
kdouble=3.7273
Hall angle, Anomalous Hall effect (AHE), Inverse Spin Hall effect (Sample dependence) |
details of this measurement method is here |
| Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
The Hall angle αHall , its 1st derivation ∂αHall/∂Hz and its 2d derivation ∂2αHall/∂Hz2 is simultaneously fitted by equation (See here)
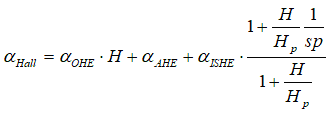
where αOHE is Hall angle of Ordinary Hall effect, αAHE is Hall angle of Anomalous Hall effect and where αISHE is Hall angle of Inverse Spin Hall effect
There is an ambiguity for αISHE and αAHE, which depends on unknown spin polarization sp
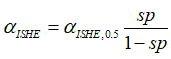
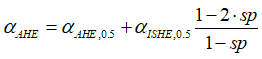
where sp is the spin polarization of conduction electrons, αAHE,0.5 is αAHE at sp=0.5, αISHE,0.5 is αISHE at sp=0.5
sample:( free35 gate) ![]() αISHE,0.5= 187 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1513 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=8.41 kG;
αISHE,0.5= 187 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1513 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=8.41 kG;
sample:( free36 gate) ![]() αISHE,0.5= 213 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1777 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=9.72 kG;
αISHE,0.5= 213 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1777 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=9.72 kG;
sample:( free56 gate) ![]() αISHE,0.5= 207 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1980mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=9.5 kG;
αISHE,0.5= 207 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 1980mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=9.5 kG;
sample:( free82 gate) ![]() αISHE,0.5= 284 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 2701 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=10.83 kG;
αISHE,0.5= 284 mdeg; αAHE,0.5= 2701 mdeg; αOHE=0.2 mdeg/kG; Hp=10.83 kG;
 AHE & ISHE
AHE & ISHE
Spin-orbit torque. Hall angle, Anomalous Hall effect (AHE), Inverse Spin Hall effect vs current |
details of this measurement method is here |
| Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
(temperature) ![]()
(AHE vs I2 ): strong 2.5-4 % decrease at current of 100 mA/ μm2; 1-2.5 % decrease at current of 50 mA/ μm2
(ISHE vs I2 ): weak; strange polarity
(Spin- orbit torque) ![]()
(AHE(I)-AHE(-I)): moderate ~0.5 % ; slope: all negative; saturation: at 50 mA/ μm2;
(ISHE(I)-ISHE(-I)): very small (0.04 mdeg/kG)
Measurement of PMA. Anisotropy field |
details of this measurement method is here |
| Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Spin-orbit torque. Measurement of dependence of PMA on the electrical current j. |
details of this measurement method is here |
| Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
Spin-orbit torque. Measurement of dependence of anisotropy field Hanis and offset magnetic field Hoff on the electrical current j. |
Data of Sample free36 gate |
| details of this measurement method is here |
| click on image to enlarge it |
SOT effect. Current dependence of magnetization switching parameters. |
details of this measurement method is here |
| Sample Volt50: Ta(3 nm)/ FeB(1.1 nm)/ MgO(7 nm)/ W(1 nm) /Ru(5 nm) |
| click on image to enlarge it |
![]()
![]() I am strongly against a fake and "highlight" research
I am strongly against a fake and "highlight" research ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
I will try to answer your questions as soon as possible